Advancements in Betulinic Acid-Loaded Nanoformulations for Enhanced Anti-Tumor Therapy
- PMID: 39748899
- PMCID: PMC11694648
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S493489
Advancements in Betulinic Acid-Loaded Nanoformulations for Enhanced Anti-Tumor Therapy
Abstract
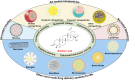
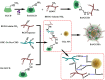
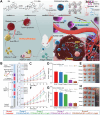
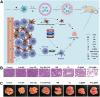
Betulinic acid (BA) is a natural compound obtained from plant extracts and is known for its diverse pharmacological effects, including anti-tumor, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and anti-atherosclerotic properties. Its potential in anti-tumor therapy has garnered considerable attention, particularly for the treatment of breast, lung, and liver cancers. However, the clinical utility of BA is greatly hindered by its poor water solubility, low bioavailability, and off-target toxicity. To address these issues, researchers have developed various BA-loaded nanoformulations, such as nanoparticles, liposomes, micelles, and nanofibers, aiming to improve its solubility and bioavailability, prolong plasma half-life, and enhance targeting ability, thereby augmenting its anti-cancer efficacy. In preparing this review, we conducted extensive searches in well-known databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect, using keywords like "betulinic acid", "nanoparticles", "drug delivery", "tumor", and "cancer", covering the literature from 2014 to 2024. The review provides a comprehensive overview of recent advancements in the application of BA-loaded nano-delivery systems for anti-tumor therapy and offers insights into their future development prospects.
Keywords: anti-tumor; betulinic acid; bioavailability; nanoformulations; targeting.
© 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
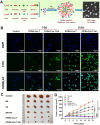
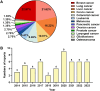
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

