The Intelligence Structures of School-Age Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study in China
- PMID: 39748915
- PMCID: PMC11694017
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S489365
The Intelligence Structures of School-Age Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study in China
Abstract
Purpose: There is no consensus on whether cognitive measures among attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) subtypes exhibit more similarities or differences, and most of them have been conducted on English-speaking subjects, lacking cross-cultural perspectives. The present study was aimed at investigating the intelligence structures of school-age children with ADHD who speak Chinese, using a multicenter and large sample size approach, offering some references for clinicians.
Patients and methods: 772 children aged 6 to 12 years with ADHD took part in the cross-sectional study. All participants underwent the Chinese Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Third Edition assessment. Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) Statistics 24 was used for statistical analyses.
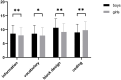
Results: No significant differences were found in full intelligence quotient (FIQ), verbal IQ (VIQ), performance quotient (PIQ), as well as most subtest scores among ADHD subtypes. The analysis of variance showed that the boys' scores were higher than girls' scores in PIQ (P < 0.05), information (P < 0.01), vocabulary (P < 0.05) and block design (P<0.01) from the perspective of sex, but lower in the coding (P < 0.01). From the perspective of age, the senior group (aged 9-12) scored higher in block design (P < 0.01) and object assembly (P < 0.05) than the junior one (aged 6-8), but lower in VIQ (P < 0.05) and verbal comprehension (VC) factor.
Conclusion: Our study supported that ADHD substyles shared more similarities in intelligence structures. Boys outperformed girls in PIQ and some subtests, suggesting that the importance to consider the gender differences and the distribution of intellectual strengths and weaknesses. Older children outperformed in block design and object assembly, but underperformed in VIQ and VC factor. This indicated the need to focus on language development and screen for specific learning disabilities in managing school-age children with ADHD.
Keywords: ADHD; intellectual strengths and weaknesses; intelligence structures; language development; school-age children.
© 2024 Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Çelik C, Erden G, Özmen S, Tural Hesapçıoğlu S. Comparing two editions of Wechsler Intelligence Scales and assessing reading skills in children with attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder. Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 2017;28(2):104–116. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

