Real-world clinical results of CGRP monoclonal antibody treatment for medication overuse headache of migraine without abrupt drug discontinuation and no hospitalization
- PMID: 39748981
- PMCID: PMC11693917
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40190
Real-world clinical results of CGRP monoclonal antibody treatment for medication overuse headache of migraine without abrupt drug discontinuation and no hospitalization
Abstract
Background: Abrupt discontinuation of overused medications is standard treatment for medication overuse headache (MOH), but discontinuation is difficult to maintain. The aim was to evaluate the real-world clinical results of anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibody (CGRP-mAb) treatment for migraine with MOH without abrupt drug discontinuation and no hospitalization.
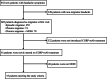
Methods: Data were collected before starting CGRP-mAb injections (baseline) and 1 month after each injection. The following items were compared between baseline and after the first, second, and third CGRP-mAb injections, monthly headache days (MHD), monthly migraine days (MMD), monthly acute medication use (AMU) days, monthly total amount of AMU tablets, headache impact test-6 (HIT-6), and the migraine-specific quality of life questionnaire (MSQ). Achieving reduction rates ≥50 % in the frequency of each headache and migraine was defined as a good response. Achieving reduction rates of both AMU days and tablets ≥50 % was defined as effective in reducing AMU.
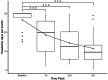
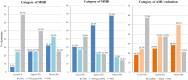
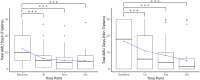
Results: This study included 33 patients with migraine with MOH. After the third CGRP-mAb injection, MHD and MMD were significantly decreased from median 30.0 to 9.5 days, and 10.0 to 1.5 days, respectively. In addition, monthly AMU days and tablets were significantly decreased from median 28.0 to 8.0 days, and 30.0 to 9.5 tablets, respectively. After the third CGRP-mAb injection, the good MHD and MMD responder rates were 75.0 % and 85.7 %, respectively. The rate of reducing AMU was 78.6 %. HIT-6 and MSQ scores decreased significantly from baseline to after each CGRP-mAb injection.
Conclusions: When CGRP-mAb was administered to migraine with MOH, frequency of headache symptoms and AMU were reduced without abrupt drug discontinuation and no hospitalization.
Keywords: Acute medication use; CGRP; Discontinuation; Hospitalization; MOH; Migraine; Monoclonal antibody.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
TT received speaking fees from Daiichi Sankyo, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, and Amgen. YF reports no conflict of interest. SM reports no conflict of interest. YN reports no conflict of interest. TI reports no conflict of interest. YN reports no conflict of interest. MM reports no conflict of interest. YI reports no conflict of interest. MH reports no conflict of interest. TS reports no conflict of interest. SY reports no conflict of interest. TW reports no conflict of interest. RS received speaking fees from Daiichi Sankyo.
Figures
References
-
- Ashina M., Katsarava Z., Do T.P., Buse D.C., Pozo-Rosich P., Özge A., Krymchantowski A.V., Lebedeva E.R., Ravishankar K., Yu S., Sacco S., Ashina S., Younis S., Steiner T.J., Lipton R.B. Migraine: epidemiology and systems of care. Lancet. 2021;397:1485–1495. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32160-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

