Adapting a Longitudinal Structured Program to Enhance Research Skills in Undergraduate Medical Students: A Key Advancement in Competency-Based Medical Education
- PMID: 39749166
- PMCID: PMC11691099
- DOI: 10.4103/ijabmr.ijabmr_219_24
Adapting a Longitudinal Structured Program to Enhance Research Skills in Undergraduate Medical Students: A Key Advancement in Competency-Based Medical Education
Abstract
Background: Abundant literature signifies the imperative role of evidence-based research in the health sector which underpins the importance of training medical graduates in research skills early in their medical journey. Low awareness, less knowledge, and minimal practical involvement of undergraduates (UGs) in research have been identified all over India. The lack of structured delivery of research curriculum in the UG period has been the basis of uptaking this project with the aim of developing research competency in medical UGs.
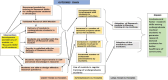
Materials and methods: The study was conducted as a participatory action research with a mixed-method approach in the department of community medicine at a medical college. A structured validated module was developed by the core committee and then pilot tested. The 5 years' journey through module development, pilot testing, longitudinal delivery, and then adapting it into a value-added course program at the university curriculum level was attempted.
Results: "UG Medical Research" has been adopted as value-added course in the curriculum of MBBS in the university. The research program is being run in a longitudinal structured manner with all MBBS UGs being trained using the "Module for UG Medical Research" module followed by research mentoring by faculty and subsequently academic scholarships in Electives Research Block 1. Interdisciplinary voluntary faculty pool has been created for research mentoring of UG students. The research environment of the institute has improved in terms of the increase in the number of research projects being carried out by UG students, Short Term Studentship (STS) Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) research scholarships, conducting annual UG research exhibition/conferences in the campus, awards for best research works, and providing intramural research grant for UGs.
Conclusions: The longitudinal structured research program was successfully incorporated into the UG curriculum which enabled UG students to demonstrate acquisition of research competency.
Keywords: Competency-based medical education; medical undergraduates; research skills; structured longitudinal program.
Copyright: © 2024 International Journal of Applied and Basic Medical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bornstein BH, Emler AC. Rationality in medical decision making: A review of the literature on doctors’ decision-making biases. J Eval Clin Pract. 2001;7:97–107. - PubMed
-
- Ghali WA, Saitz R, Eskew AH, Gupta M, Quan H, Hershman WY. Successful teaching in evidence-based medicine. Med Educ. 2000;34:18–22. - PubMed
-
- Habib SR, AlOtaibi SS, Abdullatif FA, AlAhmad IM. Knowledge and attitude of undergraduate dental students towards research. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2018;30:443–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources