The Empathy Quandary in Postgraduate Medical Training
- PMID: 39749171
- PMCID: PMC11691101
- DOI: 10.4103/ijabmr.ijabmr_288_24
The Empathy Quandary in Postgraduate Medical Training
Abstract
Background: Empathy stands as a cornerstone of humanistic qualities and is essential in healthcare for understanding and alleviating emotional suffering. Despite its necessity, formal empathy training remains elusive in postgraduate medical education across the globe, contributing to decline of humanistic practice among trainees. This study aims to assess and establish the need for empathy training by evaluating the perspectives of postgraduate trainees and faculty.
Materials and methods: The study was conducted in a medical college of western India in 2023. Three online validated questionnaires were used to assess empathy-related perceptions among faculty and postgraduate trainees across various specialties. The questionnaires focused on demographic data, importance of empathy in patient care, empathy training, perceived levels of empathy, reasons for shortfalls in empathetic behavior and recommendations for nurturing empathy. Data were analyzed quantitatively and thematically.
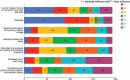
Results: A total of 150 and 127 responses were gathered and analyzed from faculty and trainees, respectively. Excessive workload, lack of formal training, and technology-dependent fast paced lifestyle were attributed for lack of empathy in clinical care. All the faculty agreed that empathy training is essential and majority (67%) believed that lack of empathetic behavior led to dissatisfaction among patients and caregivers.
Conclusion: Empathetic communication and behaviors are fundamental competencies for health-care professionals. There is need for a structured training for empathy in postgraduate medical curriculum.
Keywords: Empathy; hidden curriculum; humanities; postgraduate trainee.
Copyright: © 2024 International Journal of Applied and Basic Medical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nurturing Empathy through Arts, Literature, and Role Play for Postgraduate Trainees of Ophthalmology.Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2024 Jan-Mar;14(1):42-47. doi: 10.4103/ijabmr.ijabmr_454_23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38504843 Free PMC article.
-
What impact does postgraduate clinical training have on empathy among Japanese trainee dentists?BMC Med Educ. 2021 Jan 14;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02481-y. BMC Med Educ. 2021. PMID: 33446194 Free PMC article.
-
Humanistic medicine in anaesthesiology: development and assessment of a curriculum in humanism for postgraduate anaesthesiology trainees.Br J Anaesth. 2019 Dec;123(6):887-897. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2019.08.021. Epub 2019 Oct 5. Br J Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 31591019 Free PMC article.
-
Empathy Among Orthopaedic Surgery Trainees.JB JS Open Access. 2021 Sep 9;6(3):e21.00041. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.OA.21.00041. eCollection 2021 Jul-Sep. JB JS Open Access. 2021. PMID: 34522833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health informatics competencies in postgraduate medical education and training in the UK: a mixed methods study.BMJ Open. 2019 Mar 30;9(3):e025460. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025460. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30928942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clark A. Empathy and Alfred Adler: An integral perspective. J Individ Psychol. 2016;72:237–53.
-
- Dohrenwend AM. Defining empathy to better teach, measure, and understand its impact. Acad Med. 2018;93:1754–6. - PubMed
-
- Goleman D. What makes a leader? Harv Bus Rev. 1998;76:93–102. - PubMed
-
- Derksen FA, Olde Hartman TC, Lagro-Janssen AL, Kramer AW. Clinical empathy in GP-training: Experiences and needs among Dutch GP-trainees. “Empathy as an element of personal growth”. Patient Educ Couns. 2021;104:3016–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources