ABCA1 promote tumor environment heterogeneity via epithelial mesenchymal transition in Huh7 and HepG2 liver cancer cell
- PMID: 39749197
- PMCID: PMC11693991
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1498528
ABCA1 promote tumor environment heterogeneity via epithelial mesenchymal transition in Huh7 and HepG2 liver cancer cell
Abstract
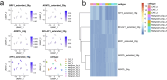
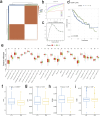
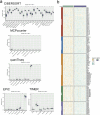
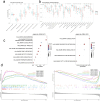
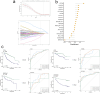
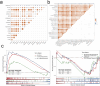
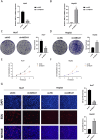
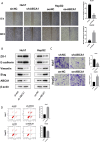
In this study, we delve into the intrinsic mechanisms of cell communication in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Initially, employing single-cell sequencing, we analyze multiple malignant cell subpopulations and cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF) subpopulations, revealing their interplay through receptor-ligand interactions, with a particular focus on SPP1. Subsequently, employing unsupervised clustering analysis, we delineate two clusters, C1 and C2, and compare their infiltration characteristics using various tools and metrics, uncovering heightened cytotoxicity and overall invasion abundance in C1. Furthermore, our gene risk scoring model indicates heightened activity of the immune therapeutic pathway in C1. Lastly, employing a formulated scoring system, we stratify patients into high and low-risk groups, revealing notably poorer outcomes in the high-risk cohort on Kaplan-Meier curves. Risk scores exhibit a negative correlation with model genes and immune cell infiltration scores, indicating poor prognosis in the high-risk group. Further characterization elucidates the regulatory landscape of the high and low-risk groups across various signaling pathways. In addition, we used wet lab experiments to prove that ABCA1 plays a pro-oncogenic role in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by promoting proliferation, invasion, migration, and reducing apoptosis. In summary, these findings provide crucial insights, offering valuable clues and references for understanding HCC pathogenesis and patient prognosis.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; immune therapeutic pathway; risk stratification; single-cell sequencing; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2024 Yu, Guo, Zhang, Yu, Wang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chen D., Liu J., Zang L., Xiao T., Zhang X., Li Z., et al. (2022). Integrated machine learning and bioinformatic analyses constructed a novel stemness-related classifier to predict prognosis and immunotherapy responses for hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 18 (1), 360–373. 10.7150/ijbs.66913 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

