Stratifying vascular disease patients into homogeneous subgroups using machine learning and FLAIR MRI biomarkers
- PMID: 39749287
- PMCID: PMC11688236
- DOI: 10.1038/s44303-024-00063-x
Stratifying vascular disease patients into homogeneous subgroups using machine learning and FLAIR MRI biomarkers
Abstract
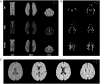
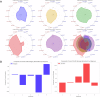
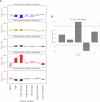
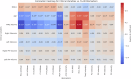
This study proposes a framework to stratify vascular disease patients based on brain health and cerebrovascular disease (CVD) risk using regional FLAIR biomarkers. Intensity and texture biomarkers were extracted from FLAIR volumes of 379 atherosclerosis patients. K-Means clustering identified five homogeneous subgroups. The 15 most important biomarkers for subgroup differentiation, identified via Random Forest classification, were used to generate biomarker profiles. ANOVA tests showed age and white matter lesion volume were significantly (p < 0.05) different across subgroups, while Fisher's tests revealed significant (p < 0.05) differences in the prevalence of several vascular risk factors across subgroup. Based on biomarker and clinical profiles, Subgroup 4 was characterized with neurodegeneration unrelated to CVD, Subgroup 3 identified patients with high CVD risk requiring aggressive intervention, and Subgroups 1, 2, and 5 identified patients with varying levels of moderate risk, suitable for long-term lifestyle interventions. This study supports personalized treatment and risk stratification based on FLAIR biomarkers.
Keywords: Brain imaging; Image processing.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- The Burden of Cerebrovascular Disease in the United States. Accessed May 11, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2019/18_0411.htm
-
- Bonberg, N., Wulms, N., Dehghan-Nayyeri, M., Berger, K. & Minnerup, H. Sex-Specific Causes and Consequences of White Matter Damage in a Middle-Aged Cohort. Front. Aging Neurosci.14, 810296 (2022). Accessed January 29, 2024. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2022.810296. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
