Analyzing the non-linear relationship between fasting blood glucose levels and Gensini score in patients with STEMI
- PMID: 39749314
- PMCID: PMC11693739
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1427567
Analyzing the non-linear relationship between fasting blood glucose levels and Gensini score in patients with STEMI
Abstract
Background: Acute myocardial infarction (AMI), particularly ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), significantly impacts global health, exacerbated by risk factors such as diabetes mellitus (DM). While the Gensini score effectively quantifies coronary artery lesions, its correlation with fasting blood glucose (FBG) levels, particularly in a non-linear fashion, has not been thoroughly explored in STEMI patients.
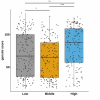
Methods: This study analyzed data from 464 STEMI patients treated with percutaneous coronary intervention at the First People's Hospital of Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province, China, from January 2010 to October 2014. We stratified patients into three FBG tertiles and utilized multiple statistical analyses, including least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression and curve fitting, to examine the potential U-shaped relationship between FBG levels and Gensini scores.
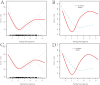
Results: Our analysis revealed significant differences in Gensini scores across FBG tertiles, with both hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic extremes showing higher scores compared to the normoglycemic range. The curve fitting analysis confirmed a U-shaped relationship, suggesting a significant, non-linear association between FBG levels and coronary artery lesion severity, regardless of diabetes status.
Conclusions: Our findings underscore the complexity of glycemic control in STEMI management and suggest that both hypo- and hyperglycemia are significant risk factors for severe coronary lesions as quantified by the Gensini score. This study highlights the importance of comprehensive FBG monitoring and management to improve outcomes for STEMI patients.
Keywords: Gensini score; ST-elevation myocardial infarction; acute myocardial infarction; diabetes mellitus; fasting blood glucose.
© 2024 Li, Lin, Jiang and Zhong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

