Prognostic potential of inflammatory markers in chronic kidney disease patients combined with acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 39749315
- PMCID: PMC11693649
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1430215
Prognostic potential of inflammatory markers in chronic kidney disease patients combined with acute myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: Inflammation significantly impacts chronic kidney disease (CKD) and acute myocardial infarction (AMI). This study investigates the prognostic value of inflammatory markers in predicting outcomes for CKD patients with AMI.
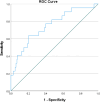
Methods: We enrolled patients diagnosed with CKD concomitant with AMI, choosing five inflammatory markers related to both diseases. Patients were categorized into elevated inflammatory markers group and control group based on inflammatory markers cut-off values for predicting in-hospital major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE). Using univariate and multivariate logistic regression, we identified inflammation-related risk factors for MACCE. We adjusted covariates stepwise to explore the relationship between independent risk factors and adverse outcomes. We also evaluated the predictive value of these markers for MACCE by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Results: In the multivariate logistic regression analysis, higher levels of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) significantly increased risk of MACCE (all P < 0.05). After adjusting above two indicators, NLR was independently associated with in-hospital MACCE in CKD patients with AMI (OR = 10.764, 95% CI: 1.887-61.406, P = 0.007). Furthermore, compared to other inflammatory markers, NLR had the highest predictive value for MACCE in patients with AMI and CKD [Area Under the Curve (AUC): 0.748, 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 0.634-0.861, P < 0.001].
Conclusion: In CKD patients combined with AMI, elevated levels of inflammation markers could increase the risk of MACCE. NLR may provide superior predictive value compared to other markers.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; chronic kidney disease; inflammatory markers; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; prognosis.
© 2024 Dang, Li and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognostic potential of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet to lymphocyte ratio, and monocyte to lymphocyte ratio in acute myocardial infarction patients combined with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jul 12;11:1401634. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1401634. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39070559 Free PMC article.
-
[Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio on long-term outcomes of acute myocardial infarction patients with multivessel disease].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2019 Jan 24;47(1):42-48. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2019.01.005. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30669809 Chinese.
-
The use of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T and creatinine kinase-MB as a prognostic markers in patients with acute myocardial infarction and chronic kidney disease.Ren Fail. 2023 Dec;45(1):2220420. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2220420. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37278148 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of inflammatory markers for all-cause mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction in the coronary care unit: a retrospective study based on MIMIC-IV database.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jan 22;12:1439650. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1439650. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 39911562 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in the application of novel inflammatory indicators in chronic kidney disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 30;12:1500166. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1500166. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39950124 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

