Emerging Wearable Acoustic Sensing Technologies
- PMID: 39749384
- PMCID: PMC11809411
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202408653
Emerging Wearable Acoustic Sensing Technologies
Abstract
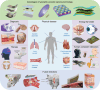
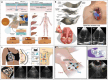
Sound signals not only serve as the primary communication medium but also find application in fields such as medical diagnosis and fault detection. With public healthcare resources increasingly under pressure, and challenges faced by disabled individuals on a daily basis, solutions that facilitate low-cost private healthcare hold considerable promise. Acoustic methods have been widely studied because of their lower technical complexity compared to other medical solutions, as well as the high safety threshold of the human body to acoustic energy. Furthermore, with the recent development of artificial intelligence technology applied to speech recognition, speech recognition devices, and systems capable of assisting disabled individuals in interacting with scenes are constantly being updated. This review meticulously summarizes the sensing mechanisms, materials, structural design, and multidisciplinary applications of wearable acoustic devices applied to human health and human-computer interaction. Further, the advantages and disadvantages of the different approaches used in flexible acoustic devices in various fields are examined. Finally, the current challenges and a roadmap for future research are analyzed based on existing research progress to achieve more comprehensive and personalized healthcare.
Keywords: acoustic sensor; human‐machine interface; ultrasonic healthcare; wearable and implantable.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
















References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
