The new thiazolidine-2,4-dione-based hybrids with promising antimycobacterial activity: design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and drug interaction analysis
- PMID: 39749402
- PMCID: PMC11703137
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2024.2442703
The new thiazolidine-2,4-dione-based hybrids with promising antimycobacterial activity: design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and drug interaction analysis
Abstract
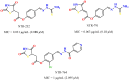
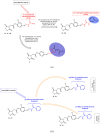
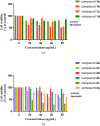
The ever-increasing drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB) has invigorated the focus on the discovery and development of novel therapeutic agents and treatment options. Thiazolidinone-based compounds have shown good antitubercular properties in vitro. Here, we report the design and synthesis of a number of new derivatives inspired by the structure of thiazolidine-2,4-dione (TZD). The TZD-based hybrids with the thiosemicarbazone or the pyridinecarbohydrazone moiety were synthesised and their antimycobacterial activity was investigated against the reference H37Rv and two wild Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) strains. In further studies, a two-drug interaction analysis was also performed for assessing their synergism with the current first-line drugs used for the treatment of TB. It was found that some of the compounds showed high antimycobacterial activity with MICs (0.078-0.283 µM) and a synergistic effect with isoniazid or rifampicin, thereby demonstrating their potential as a promising scaffold for the development of novel coadjuvants for the effective treatment of TB.
Keywords: Thiazolidine-2,4-diones; antimycobacterial activity; cytotoxicity; structure–activity relationship; synergism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Coronavirus (COVID-19). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2023. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2023. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
-
- Tiberi S, Muñoz-Torrico M, Duarte R, Dalcolmo M, D’Ambrosio L, Migliori G-B.. New drugs and perspectives for new anti-tuberculosis regimens. Pulmonology. 2018;24(2):86–98. - PubMed
-
- WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: treatment – drug-susceptible tuberculosis treatment. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
