The Effect of APOE ε4 on Alzheimer's Disease Fluid Biomarkers: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on the COAST
- PMID: 39749650
- PMCID: PMC11696244
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.70202
The Effect of APOE ε4 on Alzheimer's Disease Fluid Biomarkers: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on the COAST
Abstract
Aims: To analyze the effect of APOE ε4 on fluid biomarkers and the correlations between blood molecules and CSF biomarkers in AD patients.
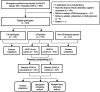
Methods: This study enrolled 575 AD patients, 131 patients with non-AD dementia, and 112 cognitively normal (CN) participants, and AD patients were divided into APOE ε4 carriers and non-carriers. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers and blood-derived biomolecules were compared between AD and CN groups, between non-AD dementia and CN groups, as well as within APOE ε4 subgroups of AD patients. Utilizing Spearman's correlation analysis and quantile regression analysis, the relationships between blood-derived biomolecules and CSF biomarkers were analyzed in APOE ε4 carriers and non-carriers.
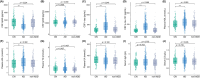
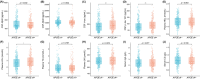
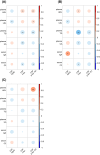
Results: The levels of CSF biomarkers and blood molecules exhibited significant differences between the AD and CN groups, including Aβ42, t-tau, p-tau 181, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and uric acid. In AD patients, APOE ε4 carriers had increased levels of CSF t-tau, p-tau 181, and plasma LDL. In the correlation and regression analyses, the negative relationships between plasma TG and t-tau, between plasma TG and p-tau 181 levels, as well as the positive relationship between serum IgA and CSF Aβ42, were observed significantly in APOE ε4+ AD groups, but not in APOE ε4- AD group.
Conclusion: APOE ε4 is associated with accelerated progression of AD pathology. The blood-derived biomolecules correlated with CSF biomarkers in APOE ε4 carriers are related to neuroinflammation and lipid metabolism, which may indicate the role of APOE ε4 in AD pathophysiology and offer insights for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for AD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03653156.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; apolipoprotein E; biomarker; high‐density lipoprotein; immunoglobulin; low‐density lipoprotein; uric acid.
© 2025 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D., et al., “Association of Apolipoprotein E Allele ϵ4 With Late‐Onset Familial and Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease,” Neurology 43, no. 8 (1993): 1467–1472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

