Aquaporin‑1 regulates microglial polarization and inflammatory response in traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 39749692
- PMCID: PMC11759584
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5482
Aquaporin‑1 regulates microglial polarization and inflammatory response in traumatic brain injury
Abstract
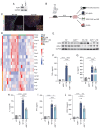
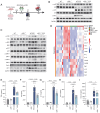
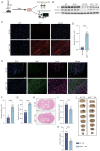
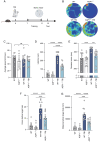
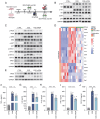
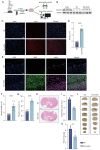
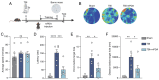
The present study investigated the mechanisms by which aquaporin 1 (AQP1) influences microglial polarization and neuroinflammatory processes in traumatic brain injury (TBI). A model of TBI was generated in AQP1‑knockout mice to assess the impact of AQP1 deletion on inflammatory cytokine release, neuronal damage and cognitive function. Immunofluorescence, reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR, western blotting and enzyme‑linked immunosorbent assay were employed to evaluate pro‑inflammatory and anti‑inflammatory markers. Behavioral assessments, including the Barnes maze, were performed to determine cognitive outcomes. Moreover, AQP1 knockout inhibited the activation of inflammation‑related signaling pathways, including nuclear factor‑κB, Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription, phosphoinositide 3‑kinase/protein kinase B and extracellular signal‑regulated kinase/mitogen‑activated protein kinase pathways. Further studies indicated that the AQP1 inhibitor m‑phenylenediacrylic acid demonstrated significant neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of TBI. These findings suggested that AQP1 may be essential in post‑TBI inflammatory responses and neuronal injury, establishing a theoretical foundation for future therapies aimed at AQP1.
Keywords: AQP1; TBI; inflammation; microglia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
