Effectiveness and Safety of Treatments for Early-Stage Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Non-Randomized Studies
- PMID: 39749718
- PMCID: PMC11696246
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.70553
Effectiveness and Safety of Treatments for Early-Stage Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Non-Randomized Studies
Abstract
Objective: The lack of consensus on the benefits and harms of standard therapies, including surgery (SRx), radiotherapy (RTx), chemotherapy (CTx), and their combinations among early-stage MCC, prompted this study.
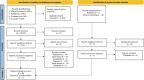
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and non-randomized studies published between January 01, 1972, and January 31, 2023, and having overall survival (OS), local recurrence (LR), regional recurrence (RR), disease-specific survival (DSS), and/or disease-free survival (DFS) as outcomes was conducted using the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), PubMed (NCBI), Scopus (ELSEVIER), and Web of Science (CLAVIRATE) databases. Hazard ratios (HRs) and their variances were pooled using the inverse variance heterogeneity model.
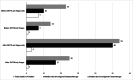
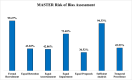
Results: Forty-nine studies representing 46,215 participants were included in the meta-analysis. A statistically significant improvement in OS was observed for groups administered adjuvant RTx (SRx + RTx) compared to SRx only (HR = 0.78, 95% CI, 0.62-0.99), albeit with statistically significant heterogeneity (Q = 532.30, p < 0.001) and a large amount of inconsistency (I2 = 94%, 95% CI, 93.0-95.5). Both LR (HR = 1.52, 95% CI, 0.37-6.19) and RR (HR = 0.41, 95% CI, 0.09-1.78) were not statistically significant. In addition, DSS (HR = 0.58, 95% CI, 0.24-1.40) was not statistically significant but DFS was (HR = 0.35, 95% CI, 0.13-0.93). Subgroup analyses revealed that adjuvant radiotherapy was more effective in local than regional MCC. The E-value suggested that the RTx dose was a confounder of the observed effectiveness of adjuvant RTx; and also, the use of CTx following adjuvant RTx, did not impact the strength of evidence for OS.
Conclusions: Although adjuvant RTx improves survival and recurrence outcomes among early-stage MCC, the safety and effectiveness of standard therapies in MCC remains poorly studied and, thus, affects the synthesis of evidence across important patient and clinical characteristics. Future research on the comparative effectiveness of different therapies is needed.
Keywords: Merkel cell carcinoma; disease‐free survival; disease‐specific survival; local recurrence; meta‐analysis; overall survival; regional recurrence.
© 2025 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy in rectal cancer operated for cure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Mar 14;2012(3):CD004078. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004078.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22419291 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment options for progression or recurrence of glioblastoma: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 4;5(1):CD013579. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013579.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34559423 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy for early stage cervical cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 22;11(11):CD005342. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005342.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27873308 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant treatment for stage III and IV cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 17;1(1):CD012974. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012974.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36648215 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Understanding Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Pathogenic Signaling, Extracellular Matrix Dynamics, and Novel Treatment Approaches.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 2;17(7):1212. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071212. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227764 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fidanzi C., Troaca S. F., Fanelli G. N., et al., “Epidemiology of Merkel Cell Carcinoma in Tuscany (Italy), 2006–2021,” European Journal of Cancer Prevention 32, no. 3 (2023): 298–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

