Retinal dysfunction in APOE4 knock-in mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39749840
- PMCID: PMC11848189
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14433
Retinal dysfunction in APOE4 knock-in mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
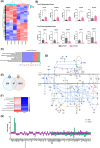
Introduction: Late-onset Alzheimer's Disease (LOAD) is the predominant form of Alzheimer's disease (AD), and apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 is a strong genetic risk factor for LOAD. As an integral part of the central nervous system, the retina displays a variety of abnormalities in LOAD. Our study is focused on age-dependent retinal impairments in humanized APOE4-knock-in (KI) and APOE3-KI mice developed by the Model Organism Development and Evaluation for Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease (MODEL-AD) consortium.
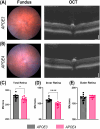
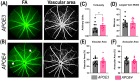
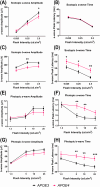
Methods: All the experiments were performed on 52- to 57-week-old mice. The retina was assessed by optical coherence tomography, fundoscopy, fluorescein angiography, electroretinography, optomotor response, gliosis, and neuroinflammation. mRNA sequencing was performed to find molecular pathways.
Results: APOE4-KI mice showed impaired retinal structure, vasculature, function, vision, increased gliosis and neuroinflammation, and downregulation of synaptogenesis.
Discussion: The APOE ε4 allele is associated with increased susceptibility to retinal degeneration compared to the APOE ε3 allele.
Highlights: Apolipoprotein E (APOE)4 mice exhibit structural and functional deficits of the retina. The retinal defects in APOE4 mice are attributed to increased neuroinflammation. APOE4 mice show a unique retinal transcriptome, yet with key brain similarities. The retina offers a non-invasive biomarker for the detection and monitoring of Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: APOE; Late‐Onset Alzheimer's Disease; biomarker; retina; retinal dysfunction.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
A.B. is an ad hoc District Support Pharmacist at CVS Health/Aetna. The contents of this study do not reflect those of CVS Health/Aetna. Q.L., G.H., N.M., T.W.C., A.L.O., B.T.L., and S.A. do not have any conflicts to declare. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting information.
Figures
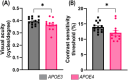

References
-
- Bales KR. The value and limitations of transgenic mouse models used in drug discovery for Alzheimer's disease: an update. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2012;7(4):281‐297. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

