Targeting IspD for Anti-infective and Herbicide Development: Exploring Its Role, Mechanism, and Structural Insights
- PMID: 39749898
- PMCID: PMC11770629
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c01146
Targeting IspD for Anti-infective and Herbicide Development: Exploring Its Role, Mechanism, and Structural Insights
Abstract
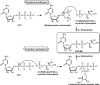
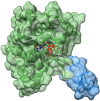
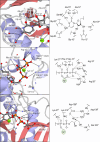
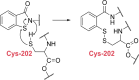
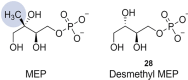
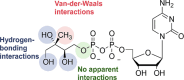
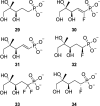
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and herbicide resistance pose threats to society, necessitating novel anti-infectives and herbicides exploiting untapped modes of action like inhibition of IspD, the third enzyme in the MEP pathway. The MEP pathway is essential for a wide variety of human pathogens, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Plasmodium falciparum, as well as plants. Within the current perspective, we focused our attention on the third enzyme in this pathway, IspD, offering a comprehensive summary of the reported modes of inhibition and common trends, with the goal to inspire future research dedicated to this underexplored target. In addition, we included an overview of the history, catalytic mechanism, and structure of the enzyme to facilitate access to this attractive target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures












References
-
- Menne H.; Köcher H. HRAC Classification of Herbicides and Resistance Development. Modern Crop Protection Compounds 2011, 5–28. 10.1002/9783527644179.ch1. - DOI
-
- Murray C. J. L.; Ikuta K. S.; Sharara F.; Swetschinski L.; Robles Aguilar G.; Gray A.; Han C.; Bisignano C.; Rao P.; Wool E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399 (10325), 629–655. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- O’Neill J.Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: final report and recommendations; Government of the United Kingdom, 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

