The molecular mechanism of gemcitabine in inhibiting the HIF-1α/VEGFB/FGF2/FGFR1 signaling pathway for ovarian cancer treatment
- PMID: 39752011
- PMCID: PMC11699178
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01723-5
The molecular mechanism of gemcitabine in inhibiting the HIF-1α/VEGFB/FGF2/FGFR1 signaling pathway for ovarian cancer treatment
Abstract
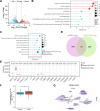
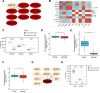
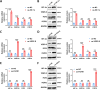
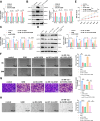
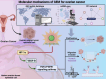
Ovarian cancer is a common malignant tumor in women, exhibiting a certain sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs like gemcitabine (GEM). This study, through the analysis of ovarian cancer single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data and transcriptome data post-GEM treatment, identifies the pivotal role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) in regulating the treatment process. The results reveal that HIF-1α modulates the expression of VEGF-B, thereby inhibiting the fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2)/FGFR1 signaling pathway and impacting tumor formation. In vitro experiments validate the mechanistic role of HIF-1α in GEM treatment, demonstrating that overexpression of HIF-1α reverses the drug's effects on ovarian cancer cells while silencing fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) can restore treatment efficacy. These findings provide essential molecular targets and a theoretical foundation for the development of novel treatment strategies for ovarian cancer in the future.
Keywords: Fibroblast growth factor 2; Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; Gemcitabine; Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha; Ovarian cancer; Vascular endothelial growth factor B.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thymoquinone affects the gemcitabine sensitivity of pancreatic cancer by regulating collagen via hypoxia inducible factor-1α.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 31;14:1138265. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1138265. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37324458 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α mediates the toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway leading to anti-tumor effects in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells under hypoxic conditions.Oncol Lett. 2016 Aug;12(2):1034-1040. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4705. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27446390 Free PMC article.
-
9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine inhibits expression of vascular endothelial growth factor through hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in human ovarian cancer cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;66(1):178-86. doi: 10.1124/mol.66.1.178. Mol Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15213310
-
4-Hydroxy estradiol but not 2-hydroxy estradiol induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor A through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/FRAP pathway in OVCAR-3 and A2780-CP70 human ovarian carcinoma cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004 Apr 1;196(1):124-35. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2003.12.002. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15050414
-
HIF-1α and VEGF Immunophenotypes as Potential Biomarkers in the Prognosis and Evaluation of Treatment Efficacy of Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review of the Literature.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025 Jan 8;30(1):27004. doi: 10.31083/FBL27004. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025. PMID: 39862086
References
-
- González-Martín A, Harter P, Leary A, et al. Newly diagnosed and relapsed epithelial ovarian cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2023;34(10):833–48. 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.07.011. - PubMed
-
- Varghese A, Lele S. Rare ovarian tumors. In: Lele S, ed. Ovarian Cancer. Brisbane (AU): Exon Publications; September 8, 2022. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
