Audio-visual concert performances synchronize audience's heart rates
- PMID: 39752187
- PMCID: PMC11776452
- DOI: 10.1111/nyas.15279
Audio-visual concert performances synchronize audience's heart rates
Abstract
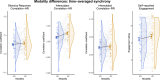
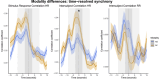
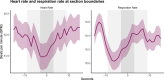
People enjoy engaging with music. Live music concerts provide an excellent option to investigate real-world music experiences, and at the same time, use neurophysiological synchrony to assess dynamic engagement. In the current study, we assessed engagement in a live concert setting using synchrony of cardiorespiratory measures, comparing inter-subject, stimulus-response, correlation, and phase coherence. As engagement might be enhanced in a concert setting by seeing musicians perform, we presented audiences with audio-only (AO) and audio-visual (AV) piano performances. Only correlation synchrony measures were above chance level. In comparing time-averaged synchrony across conditions, AV performances evoked a higher inter-subject correlation of heart rate (ISC-HR). However, synchrony averaged across music pieces did not correspond to self-reported engagement. On the other hand, time-resolved analyses show that synchronized deceleration-acceleration heart rate (HR) patterns, typical of an "orienting response" (an index of directed attention), occurred within music pieces at salient events of section boundaries. That is, seeing musicians perform heightened audience engagement at structurally important moments in Western classical music. Overall, we could show that multisensory information shapes dynamic engagement. By comparing different synchrony measures, we further highlight the advantages of time series analysis, specifically ISC-HR, as a robust measure of holistic musical listening experiences in naturalistic concert settings.
Keywords: cardiorespiratory synchrony; engagement; inter‐subject correlation; music concerts; stimulus−response correlation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The New York Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Gabrielsson, A. , & Wik, S. L. (2003). Strong experiences related to music: A descriptive system. Music & Science, 7, 157–217.
-
- Kragness , H. E. , Eitel, M. J. , Anantharajan, F. , Gaudette‐Leblanc, A. , Berezowska, B. , & Cirelli, L. K. (2023). An itsy bitsy audience: Live performance facilitates infants’ attention and heart rate synchronization. Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts, 10.1037/aca0000597 - DOI
-
- Lamont, A. (2011). University students’ strong experiences of music: Pleasure, engagement, and meaning. Music & Science, 15, 229–249.
-
- Kaneshiro, B. , Nguyen, D. T. , Norcia, A. M. , Dmochowski, J. P. , & Berger, J. (2020). Natural music evokes correlated EEG responses reflecting temporal structure and beat. Neuroimage, 214, 116559. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

