Deciphering neutrophil dynamics: Enhanced phagocytosis of elastic particles and impact on vascular-targeted carrier performance
- PMID: 39752488
- PMCID: PMC11698085
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adp1461
Deciphering neutrophil dynamics: Enhanced phagocytosis of elastic particles and impact on vascular-targeted carrier performance
Abstract
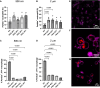
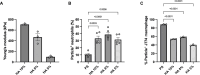
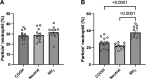
Particle elasticity has widely been established to substantially influence immune cell clearance and circulation time of vascular-targeted carriers (VTCs). However, prior studies have primarily investigated interactions with macrophages, monocytic cell lines, and in vivo murine models. Interactions between particles and human neutrophils remain largely unexplored, although they represent a critical aspect of VTC performance. Here, we explore the impact of particle elasticity on primary human neutrophil phagocytosis using polyethylene glycol-based particles of different elastic moduli. We found that neutrophils effectively phagocytose deformable particles irrespective of their modulus, indicating a departure from established phagocytosis trends seen with other types of immune cells. These findings highlight the observed phenotypic difference between different types of phagocytes and underscore the need to characterize VTC performance using various cell types and animal models that represent human systems closely.
Figures



References
-
- Key J., Palange A. L., Gentile F., Aryal S., Stigliano C., Di Mascolo D., De Rosa E., Cho M., Lee Y., Singh J., Decuzzi P., Soft discoidal polymeric nanoconstructs resist macrophage uptake and enhance vascular targeting in tumors. ACS Nano 9, 11628–11641 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Merkel T. J., Jones S. W., Herlihy K. P., Kersey F. R., Shields A. R., Napier M., Luft J. C., Wu H., Zamboni W. C., Wang A. Z., Bear J. E., DeSimone J. M., Using mechanobiological mimicry of red blood cells to extend circulation times of hydrogel microparticles. PNAS 108, 586–591 (2011). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang L., Cao Z., Li Y., Ella-Menye J.-R., Bai T., Jiang S., Softer zwitterionic nanogels for longer circulation and lower splenic accumulation. ACS Nano 6, 6681–6686 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

