Construction of exosome non-coding RNA feature for non-invasive, early detection of gastric cancer patients by machine learning: a multi-cohort study
- PMID: 39753334
- PMCID: PMC12229063
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2024-333522
Construction of exosome non-coding RNA feature for non-invasive, early detection of gastric cancer patients by machine learning: a multi-cohort study
Abstract
Background and objective: Gastric cancer (GC) remains a prevalent and preventable disease, yet accurate early diagnostic methods are lacking. Exosome non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), a type of liquid biopsy, have emerged as promising diagnostic biomarkers for various tumours. This study aimed to identify a serum exosome ncRNA feature for enhancing GC diagnosis.
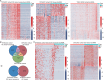
Designs: Serum exosomes from patients with GC (n=37) and healthy donors (n=20) were characterised using RNA sequencing, and potential biomarkers for GC were validated through quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) in both serum exosomes and tissues. A combined diagnostic model was developed using LASSO-logistic regression based on a cohort of 518 GC patients and 460 healthy donors, and its diagnostic performance was evaluated via receiver operating characteristic curves.
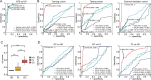
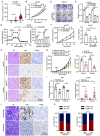
Results: RNA sequencing identified 182 candidate biomarkers for GC, of which 31 were validated as potential biomarkers by qRT-PCR. The combined diagnostic score (cd-score), derived from the expression levels of four long ncRNAs (RP11.443C10.1, CTD-2339L15.3, LINC00567 and DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene (DGCR9)), was found to surpass commonly used biomarkers, such as carcinoembryonic antigen, carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) and CA72-4, in distinguishing GC patients from healthy donors across training, testing and external validation cohorts, with AUC values of 0.959, 0.942 and 0.949, respectively. Additionally, the cd-score could effectively identify GC patients with negative gastrointestinal tumour biomarkers and those in early-stage. Furthermore, molecular biological assays revealed that knockdown of DGCR9 inhibited GC tumour growth.
Conclusions: Our proposed serum exosome ncRNA feature provides a promising liquid biopsy approach for enhancing the early diagnosis of GC.
Keywords: GASTRIC CANCER; RNA EXPRESSION; TUMOUR MARKERS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Janjigian YY, Shitara K, Moehler M, et al. First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398:27–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00797-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
