Synthesis and crystal structure of piperidinyl propanenitrile towards the preparation of piperidine based bioactive films for drug delivery applications
- PMID: 39753604
- PMCID: PMC11698915
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81996-6
Synthesis and crystal structure of piperidinyl propanenitrile towards the preparation of piperidine based bioactive films for drug delivery applications
Abstract
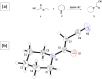
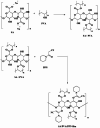
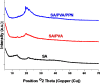
Compounds containing the piperidine group are highly attractive as building blocks for designing new drugs. Functionalized piperidines are of significant interest due to their prevalence in the pharmaceutical field. Herein, 3-oxo-3-(piperidin-1-yl) propanenitrile has been synthesized, and piperidine-based sodium alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol) films have been prepared. The polymeric films display potency and potential for application to fight against microbial infections. The films could also help maintain interaction with tissue to ensure the controlled release of therapeutic molecules. Thus, they are promising in developing drug delivery systems essential in the pharmaceutical industry. The structure of the 3-oxo-3-(piperidin-1-yl)propanenitrile was confirmed via spectroscopic and single crystal x-ray diffraction techniques. A homogenous solution of sodium alginate (SA) was used to prepare the film by the casting method in the presence of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and 3-oxo-3-(piperidin-1-yl)propanenitrile (PPN). The prepared films were characterized physiochemically via FTIR, XRD, and TGA. The film morphology was studied using SEM. The antimicrobial potency of the prepared films was assessed against various species of microorganisms. The physicochemical analysis indicated that the films were bound by chemical and physical bond formation between the cyano group of 3-oxo-3-(piperidin-1-yl)propanenitrile, methylene group of PVA, and the hydroxyl group of SA. The films showed smooth, homogenous surfaces and good mechanical properties. The results revealed that the films are bioactive, as indicated by promising antimicrobial potency against P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, E. coli, B. subtilis, and C. albicans, with high potency as well as moderate activity against A. niger. Polymeric films have promising potential to be utilized in drug delivery applications.
Keywords: Antimicrobial; Bioactive films; Crystal structure; Piperidine; Sodium alginate; Synthesis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Conception of pH-sensitive calcium alginate/poly vinyl alcohol hydrogel beads for controlled oral curcumin delivery systems. Antibacterial and antioxidant properties.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;263(Pt 2):130389. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130389. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38403207
-
Antibacterial silver nanoparticles in polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate blend produced by gamma irradiation.Int J Biol Macromol. 2015 Sep;80:170-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.06.042. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015. PMID: 26123816
-
Effect of SiO2, PVA and glycerol concentrations on chemical and mechanical properties of alginate-based films.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Feb;107(Pt B):2686-2694. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.162. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29101050
-
Papain wound dressings obtained from poly(vinyl alcohol)/calcium alginate blends as new pharmaceutical dosage form: Preparation and preliminary evaluation.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017 Apr;113:11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.12.001. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017. PMID: 27939307
-
Alginate/polyvinyl alcohol films for wound healing: Advantages and challenges.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2023 Jan;111(1):220-233. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.35146. Epub 2022 Aug 12. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2023. PMID: 35959858 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of heterocycle based carboxymethyl cellulose conjugates as novel anticancer agents targeting HCT116, MCF7, PC3 and A549 cells.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 9;15(1):29196. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14146-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40783442 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial, self-healing, and pH-responsive PVA/ZIF-8@tannic acid nanocomposite hydrogel for sustained delivery of garlic extract.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21939. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07752-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vitaku, E., Smith, D. T. & Njardarson, J. T. Analysis of the structural diversity, substitution patterns, and frequency of nitrogen heterocycles among US FDA approved pharmaceuticals: miniperspective. J. Med. Chem.57 (24), 10257–10274 (2014). - PubMed
-
- MacCoss, M., Lawson, A. & Taylor, R. Rings in drugs. J. Med. Chem.57, 5845–5859 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Greenwood, J. W. et al. Isolable iminium ions as a platform for N-(hetero) aryl piperidine synthesis. Nat. Synthesis 1–9. (2023).
-
- Liu, G. Q. & Opatz, T. Recent advances in the synthesis of piperidines: functionalization of preexisting ring systems. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem.125, 107–234 (2018).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

