Circulating tumor cell plasticity determines breast cancer therapy resistance via neuregulin 1-HER3 signaling
- PMID: 39753722
- PMCID: PMC11779641
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-024-00882-2
Circulating tumor cell plasticity determines breast cancer therapy resistance via neuregulin 1-HER3 signaling
Abstract
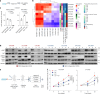
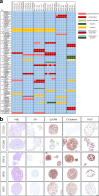
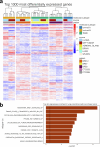
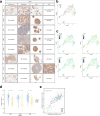
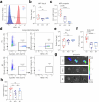
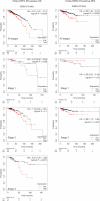
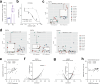
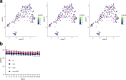
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) drive metastasis, the leading cause of death in individuals with breast cancer. Due to their low abundance in the circulation, robust CTC expansion protocols are urgently needed to effectively study disease progression and therapy responses. Here we present the establishment of long-term CTC-derived organoids from female individuals with metastatic breast cancer. Multiomics analysis of CTC-derived organoids along with preclinical modeling with xenografts identified neuregulin 1 (NRG1)-ERBB2 receptor tyrosine kinase 3 (ERBB3/HER3) signaling as a key pathway required for CTC survival, growth and dissemination. Genome-wide CRISPR activation screens revealed that fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) signaling serves a compensatory function to the NRG1-HER3 axis and rescues NRG1 deficiency in CTCs. Conversely, NRG1-HER3 activation induced resistance to FGFR1 inhibition, whereas combinatorial blockade impaired CTC growth. The dynamic interplay between NRG1-HER3 and FGFR1 signaling reveals the molecular basis of cancer cell plasticity and clinically relevant strategies to target it. Our CTC organoid platform enables the identification and validation of patient-specific vulnerabilities and represents an innovative tool for precision medicine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: B.T. and O.H. are employees of Miltenyi Biotec. Heidelberg Institute for Stem Cell Technology and Experimental Medicine (HI-STEM) has licensed the medium formulation to Miltenyi Biotec. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

