Meta-analysis of MitraClip and PASCAL for transcatheter mitral edge-to-edge repair
- PMID: 39754135
- PMCID: PMC11697868
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-024-03218-4
Meta-analysis of MitraClip and PASCAL for transcatheter mitral edge-to-edge repair
Abstract
Background: Despite the promising results of both MitraClip and PASCAL systems for the treatment of mitral regurgitation (MR), there is limited data on the comparison of both systems regarding their safety and efficacy. We aim to compare both systems for MR.
Materials and methods: Five databases were searched until October 2024. Original studies were only included and critically appraised using an adapted version of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for observational cohort studies and the Cochrane risk of bias tool for randomized controlled trials. The risk ratio (RR) and mean difference (MD) with their corresponding 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
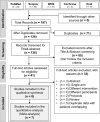
Results: From the database search, we identified 197 studies, of which eight studies comprising 1,612 patients who underwent transcatheter edge-to-edge repair with either MitraClip or PASCAL were included in this meta-analysis. The statistical analysis revealed no significant difference between the two devices in achieving a two-grade reduction in MR severity (RR = 0.95; 95% CI: [0.86, 1.04]; p = 0.28), one-grade reduction (RR = 1.17; 95% CI: [0.92, 1.49]; p = 0.19), or in cases with no improvement (RR = 1.23; 95% CI: [0.79, 1.90]; p = 0.36). Additionally, there were no significant differences between PASCAL and MitraClip regarding procedure time, procedural success, reinterventions, or all-cause mortality. However, PASCAL trended towards better residual MR reduction, although this was accompanied by moderate heterogeneity. Both devices demonstrated comparable safety profiles and were effective in reducing MR and improving cardiac function.
Conclusion: MitraClip and PASCAL devices showed comparable safety profiles and procedural success rates. However, the analysis did not reveal a statistically significant difference between the two devices in reducing the severity of MR.
Keywords: And Meta-analysis; MitraClip, PASCAL; Mitral Regurgitation; Review; Transcatheter edge-to-edge repair.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not Applicable. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



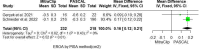

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

