Integrative multiomics reveals common endotypes across PSEN1, PSEN2, and APP mutations in familial Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39754192
- PMCID: PMC11699654
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-024-01659-6
Integrative multiomics reveals common endotypes across PSEN1, PSEN2, and APP mutations in familial Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: PSEN1, PSEN2, and APP mutations cause Alzheimer's disease (AD) with an early age at onset (AAO) and progressive cognitive decline. PSEN1 mutations are more common and generally have an earlier AAO; however, certain PSEN1 mutations cause a later AAO, similar to those observed in PSEN2 and APP.
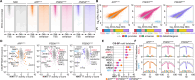
Methods: We examined whether common disease endotypes exist across these mutations with a later AAO (~ 55 years) using hiPSC-derived neurons from familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD) patients harboring mutations in PSEN1A79V, PSEN2N141I, and APPV717I and mechanistically characterized by integrating RNA-seq and ATAC-seq.
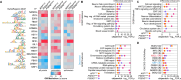
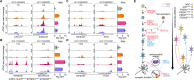
Results: We identified common disease endotypes, such as dedifferentiation, dysregulation of synaptic signaling, repression of mitochondrial function and metabolism, and inflammation. We ascertained the master transcriptional regulators associated with these endotypes, including REST, ASCL1, and ZIC family members (activation), and NRF1 (repression).
Conclusions: FAD mutations share common regulatory changes within endotypes with varying severity, resulting in reversion to a less-differentiated state. The regulatory mechanisms described offer potential targets for therapeutic interventions.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This manuscript has been reviewed by DIAN Study investigators for scientific content and consistency of data interpretation with previous DIAN Study publications. We acknowledge the altruism of the participants and their families and contributions of the DIAN research and support staff at each of the participating sites for their contributions to this study. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 CA198941/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AGO5131 , U01 NS 074501-05, R01 LM012595 , OT2 OD030544, U01 CA198941, U01 DK097430, R01 HD084633 , R01 HL106579-07,/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- STC CCF-0939370/National Science Foundation
- U01 DK097430/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS074501/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD030544/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- NIRG-14-322164/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- U19 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- SG-20-690363-DIAN/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- 1I01RX002259/U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs
- R01 HL106579/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM012595/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U19AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 RX002259/RX/RRD VA/United States
- R01 HD084633/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States

