Intelligent measurement of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis x-ray coronal imaging parameters based on VB-Net neural network: a retrospective analysis of 2092 cases
- PMID: 39754265
- PMCID: PMC11697629
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-024-05383-7
Intelligent measurement of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis x-ray coronal imaging parameters based on VB-Net neural network: a retrospective analysis of 2092 cases
Abstract
Background: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is a complex three-dimensional deformity, and up to now, there has been no literature reporting the analysis of a large sample of X-ray imaging parameters based on artificial intelligence (AI) for it. This study is based on the accurate and rapid measurement of x-ray coronal imaging parameters in AIS patients by AI, to explore the differences and correlations, and to further investigate the risk factors in different groups, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the diagnosis and surgical treatment of AIS.
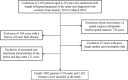
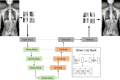
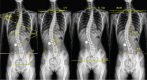
Methods: Retrospective analysis of 3192 patients aged 8-18 years who had a full-length orthopantomogram of the spine and were diagnosed with AIS at the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University from January 2019 to March 2024. After screened 2092 cases were finally included. The uAI DR scoliosis analysis system with multi-resolution VB-Net convolution network architecture was used to measure CA, CBD, CV, RSH, T1 Tilt, PT, LLD, SS, AVT, and TS parameters. The results were organized and analyzed by using R Studio 4.2.3 software.
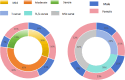
Results: The differences in CA, CBD, CV, RSH, TI tilt, PT, LLD and SS were statistically significant between male and female genders (p < 0.05); Differences in CA, CBD, T1 Tilt, PT, SS, AVT and TS were statistically significant in patients with AIS of different severity (p < 0.001), and T1 Tilt, AVT, TS were risk factors; Differences in CA, CBD, CV, RSH, T1 Tilt, PT, LLD, SS, AVT and TS were statistically significant (p < 0.05) in patients with AIS of different curve types, and TS was a risk factor; Analyzing the correlation between parameters revealed a highly linear correlation between CV and RSH (r = 0.826, p < 0.001), and a significant linear correlation between CBD and TS, and PT and SS (r = 0.561, p < 0.001; r = 0.637, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Measurements based on VB-Net neural network found that x-ray coronal imaging parameters varied among AIS patients with different curve types and severities. In clinical practice, it is recommended to consider the discrepancy in parameters to enable a more accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan.
Keywords: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis; Artificial intelligence; Intelligent measurement; VB-Net; X-ray coronal plane.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University. As this is a secondary use of previously obtained clinical data, informed consent is not required. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Xu S, Su YJ, Wang ZB, Liu CJ, Jin LY, Liu HY. Prevalence characteristics of scoliosis among primary and secondary school students in mainland China: a meta-analysis of 72 studies. China Spinal Cord J. 2021;31(10):901–10.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

