Periodic Table of Immunomodulatory Elements and Derived Two-Dimensional Biomaterials
- PMID: 39754328
- PMCID: PMC11809427
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202406324
Periodic Table of Immunomodulatory Elements and Derived Two-Dimensional Biomaterials
Abstract
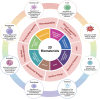
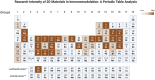
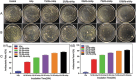
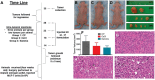
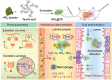
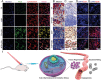
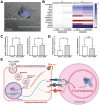
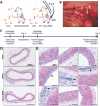
Periodic table of chemical elements serves as the foundation of material chemistry, impacting human health in many different ways. It contributes to the creation, growth, and manipulation of functional metallic, ceramic, metalloid, polymeric, and carbon-based materials on and near an atomic scale. Recent nanotechnology advancements have revolutionized the field of biomedical engineering to tackle longstanding clinical challenges. The use of nano-biomaterials has gained traction in medicine, specifically in the areas of nano-immunoengineering to treat inflammatory and infectious diseases. Two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials have been found to possess high bioactive surface area and compatibility with human and mammalian cells at controlled doses. Furthermore, these biomaterials have intrinsic immunomodulatory properties, which is crucial for their application in immuno-nanomedicine. While significant progress has been made in understanding their bioactivity and biocompatibility, the exact immunomodulatory responses and mechanisms of these materials are still being explored. Current work outlines an innovative "immunomodulatory periodic table of elements" beyond the periodic table of life, medicine, and microbial genomics and comprehensively reviews the role of each element in designing immunoengineered 2D biomaterials in a group-wise manner. It recapitulates the most recent advances in immunomodulatory nanomaterials, paving the way for the development of new mono, hybrid, composite, and hetero-structured biomaterials.
Keywords: 2D biomaterials; cancer therapy; immunoengineering; immunomodulatory periodic elements; nanomedicine; theranostic.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yin H., Xing K., Zhang Y., Dissanayake D. M. A. S., Lu Z., Zhao H., Zeng Z., Yun J.‐H., Qi D.‐C., Yin Z., Chem. Soc. Rev 2021, 50, 6423. - PubMed
-
- Smith B. R., Gambhir S. S., Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 901. - PubMed
-
- Nanocarriers as an Emerging Platform for Cancer Therapy, Jenny Stanford Publishing, Singapore, 2020.
-
- Pelaz B., Alexiou C., Alvarez‐Puebla R. A., Alves F., Andrews A. M., Ashraf S., Balogh L. P., Ballerini L., Bestetti A., Brendel C., Bosi S., Carril M., Chan W. C. W., Chen C., Chen X., Chen X., Cheng Z., Cui D., Du J., Dullin C., Escudero A., Feliu N., Gao M., George M., Gogotsi Y., Grünweller A., Gu Z., Halas N. J., Hampp N., Hartmann R. K., ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2313. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
