The financial toxicity of breast cancer: a systematic mapping of the literature and identification of research challenges
- PMID: 39754600
- PMCID: PMC11867575
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2025-0002
The financial toxicity of breast cancer: a systematic mapping of the literature and identification of research challenges
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers, increasingly prevalent also among working-age populations. Regardless of age, breast cancer has significant direct and indirect costs on the individuals, families and society. The aim of the research was to provide a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of the financial toxicity of breast cancer, to identify research voids and future research challenges.
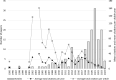
Materials and methods: The systematic mapping of literature relied on a multi-method approach, combining bibliometric methods with a standard review/discussion of most important contributions. The analysis employed Bibliometrics in R and VosViewer.
Results: The results highlighted the key authors, journals and research topics in the investigation of the financial toxicity of cancer and stressed the concentration of work around several authors and journals.
Conclusions: The results also revealed a lack of a comprehensive approach in the study of financial toxicity, as the literature often focuses on one or few selected aspects of financial toxicity. In addition, geographic coverage is uneven and differences in the healthcare systems represent a challenge to straightforward comparisons.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; breast cancer; financial toxicity.
© 2025 Ivica Ratosa et al., published by Sciendo.
Figures
References
-
- Ehsan AN, Wu CA, Minasian A, Singh T, Bass M, Pace L, et al. Financial toxicity among patients with breast cancer worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. [Internet] [2024 Mar 15];JAMA Netw Open. 2023 6:e2255388. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.55388. https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85147783077&doi=10.1... . ; : . doi: . [cited . ]. Available at: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical