Epidemiological and genetic charateristics of Vibrio vulnificus from diverse sources in China during 2012-2023
- PMID: 39755764
- PMCID: PMC11700198
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-07426-5
Epidemiological and genetic charateristics of Vibrio vulnificus from diverse sources in China during 2012-2023
Abstract
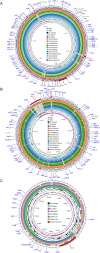
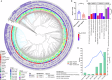
Vibrio vulnificus is a significant zoonotic pathogen that causes severe vibriosis in humans and fish. The lack of a national annual surveillance program in China has hindered understanding of its epidemiological characteristics and genetic diversity. This study characterized 150 V. vulnificus isolates collected from diverse sources in China during 2012-2023, including seafood, aquaculture water, migratory birds, marine animals, and clinical patients. Most seafood-derived isolates and all 15 clinical isolates harbored the virulence-related gene vcgC and 16S rRNA type B. The isolates exhibited diverse virulence factors (VFs), including flagella, outer membrane components, RTX toxins, and multiple secretion systems. Genes associated with the Type III secretion system were identified in migratory bird isolates, while a unique Type VI secretion system (T6SS1) were identified exclusively within a specific phylogenetic sub-lineage. T6SS1-positive strains demonstrated an increased number of genomic islands (GIs) and VFs compared to T6SS1-negative strains. Enrichment of genes related to secretion systems and biofilm formation likely facilitated the expansion of the T6SS1-positive population. The novel association between T6SS1 and a specific sub-lineage underscores potential ecological and adaptive advantages. These findings provide new insights into the ecological and evolutionary dynamics of V. vulnificus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Baker-Austin, C. et al. Vibrio spp. infections, Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers, 4, (2018) - PubMed
-
- Oliver J. D., The Biology of Vibrio vulnificus. Microbiol. Spectr., 3, 10.1128/microbiolspec.VE-0001-2014. (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

