Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 2/CCR2/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Signal Induced through Cancer Cell-Macrophage Interaction Contributes to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression
- PMID: 39756577
- PMCID: PMC12179538
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2024.12.007
Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 2/CCR2/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Signal Induced through Cancer Cell-Macrophage Interaction Contributes to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression
Abstract
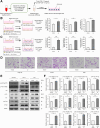
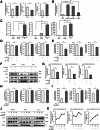
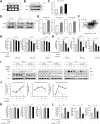
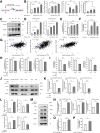
Tumor-infiltrating macrophages, known as tumor-associated macrophages, play a crucial role in the tumor microenvironment. Herein, immunohistochemistry revealed that intratumoral CD68-positive macrophages are associated with poor prognosis and clinicopathologic factors in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Subsequently, an indirect co-culture system involving HCC cells and peripheral blood-derived macrophages was developed. cDNA microarray analysis revealed that chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) was highly expressed in HCC cells co-cultured with macrophages. CCL2 neutralization suppressed proliferation, migration, and phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk) in HCC cells and macrophages enhanced through co-culture. In contrast, recombinant human CCL2 (rhCCL2) addition facilitated these malignant phenotypes and increased Erk phosphorylation levels in HCC cells and macrophages. The primary CCL2 receptor, CCR2, was expressed in HCC cells and macrophages and was up-regulated in co-cultured HCC cells. CCR2 inhibition suppressed malignant phenotypes and reduced phosphorylated levels of Erk enhanced by rhCCL2. Additionally, the inhibition of Erk signal suppressed rhCCL2-enhanced malignant phenotypes. Moreover, serum CCL2 levels were higher in patients with HCC than those in healthy donors. On the basis of immunohistochemistry, CCL2-positive cases with high CCR2 expression and phosphorylated Erk-positive cases exhibited poor survival outcomes. Therefore, CCL2 up-regulation through interactions between HCC cells and macrophages contributed to HCC progression, making the CCL2/CCR2/Erk signal a potential target for HCC treatment.
Copyright © 2025 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Statement None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemel A., Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Llovet J.M., Kelley R.K., Villanueva A., Singal A.G., Pikarsky E., Roayaie S., Lencioni R., Koike K., Zucman-Rossi J., Finn R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:6. - PubMed
-
- Müller M., Bird T.G., Nault J.C. The landscape of gene mutations in cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2020;72:990–1002. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

