Exposure to COVID-19 Pandemic-Related Stressors and Their Association With Distress, Psychological Growth and Drug Use in People With HIV in Nouvelle Aquitaine, France (ANRS CO3 AQUIVIH-NA Cohort-QuAliV-QuAliCOV Study)
- PMID: 39757312
- PMCID: PMC11985552
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-024-04588-5
Exposure to COVID-19 Pandemic-Related Stressors and Their Association With Distress, Psychological Growth and Drug Use in People With HIV in Nouvelle Aquitaine, France (ANRS CO3 AQUIVIH-NA Cohort-QuAliV-QuAliCOV Study)
Abstract
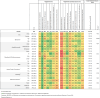
We investigated people living with HIV (PLWH)'s exposure to COVID-19 pandemic stressors and their association with distress, psychological growth, and substance use. PLWH in the ANRS CO3 AQUIVIH-NA cohort's QuAliV study (Nouvelle Aquitaine, France) completed an adapted CAIR Lab Pandemic Impact Questionnaire (C-PIQ) and reported substance use between 9/2021 to 3/2022. We described cumulative stressor exposure (score 0-16) and explored variation by PLWH characteristics (demographic, HIV-related, risk factors, psychosocial). Associations with distress (score 0-23), psychological growth (score 0-20), and substance use were assessed using regression models. Participants reported exposure to a median of 2 (IQR: 1-4) stressors. Stressor exposure was higher in working-age (<60) and psychosocially vulnerable PLWH. Exposure to an additional stressor correlated with a 0.7-point increase in distress scores (95% C.I. 0.5-1.0, p<0.001), a 0.04-point increase (95% C.I. 0.01-0.07, p=0.002) in psychological growth scores in working-age PLWH. In older PLWH, additional stressor correlated with a 0.8-point (95% C.I. 0.4-1.2, p<0.001) increase in distress and a 0.1-point increase (95% C.I. 0.06-0.2, p=0.001) in growth scores. Each additional stressor was associated with 1.2 (95% C.I. 1.0-1.4, p=0.02) higher adjusted odds of cannabis use in working-age PLWH, and 1.2 (95% C.I. 1.0-1.4, p=0.004) higher adjusted odds of drug use. Exposure to stressors was linked to increased distress, cannabis and drug use but also growth. Providers should not only be aware of risk (of severe COVID-19) but also be mindful of the social and psychological challenges PLWH face as these may affect their retention in care, especially during challenging times.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cannabis; Distress; Drugs; HIV; Psychological growth.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest in relation to this manuscript. SF has received financial support from Gilead Sciences, MSD and ViiV Healthcare to attend scientific conferences. Ethical Approval: The ANRS CO3 AQUIVIH-NA Cohort received approval from the Comité de Protection des Personnes (CPP) du Sud-Ouest et d’Outre-Mer III (25 May 2016). Patient consent statement: Informed consent was obtained from all individuals included in the cohort.
Figures
References
-
- Pratt AC. COVID – 19 impacts cities, cultures and societies. City, Cult Soc [Internet]. 2020;21:100341. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877916620300175
-
- WHO. Mental health [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2024 Oct 24]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-strengthe...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous