Chlorotoxin-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive paclitaxel delivery to Glioblastoma multiforme
- PMID: 39758413
- PMCID: PMC11699378
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41151
Chlorotoxin-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive paclitaxel delivery to Glioblastoma multiforme
Abstract
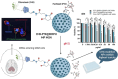
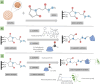
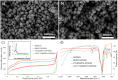
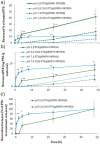
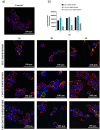
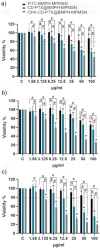
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a highly aggressive brain cancer associated with poor survival rates. We developed novel mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs)-based nanocarriers for pH-responsive delivery of a therapeutic drug Paclitaxel (PTX) to GBM tumor cells. The pores of MSNs are loaded with PTX, which is retained by β-cyclodextrin (CD) moieties covalently linked to the pore entrances through a hydrazone linkage, which is cleavable in weakly acidic environment. Furthermore, we utilized a host-guest interaction between the adamantane and capping CD moieties to further functionalize the surface with a potential glioma-targeting oligopeptide chlorotoxin (CHX). In vitro studies in the U87 GBM cell line show decreased uptake, but increased toxicity of CHX-modified nanoparticles compared to CHX-free nanoparticles. The obtained results are promising toward development of advanced drug nanocarriers, which may target the overexpressed receptors in cancer tissues and utilize their weakly acidic environment for triggering the drug release, potentially leading to more efficient cancer treatments.
Keywords: Chlorotoxin; Cyclodextrin; Glioblastoma multiforme; Mesoporous silica nanoparticles; Paclitaxel; Targeted drug delivery; pH-responsive.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thermo- and pH-responsive targeted lipid-coated mesoporous nano silica platform for dual delivery of paclitaxel and gemcitabine to overcome HER2-positive breast cancer.Int J Pharm. 2023 Dec 15;648:123606. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123606. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Int J Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37972671
-
Lipid/PAA-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for dual-pH-responsive codelivery of arsenic trioxide/paclitaxel against breast cancer cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 May;42(5):832-842. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00648-x. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 33824461 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid modified lipid-bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles co-loading paclitaxel and tanshinone IIA for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia.Int J Pharm. 2020 Aug 30;586:119576. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119576. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32603839
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018 Mar;8(2):165-177. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018. PMID: 29719777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on Recent Technologies and Patents on Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2020;14(2):126-144. doi: 10.2174/1872211314666200914155051. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2020. PMID: 32928094 Review.
References
-
- Nik A.B., Zare H., Razavi S., Mohammadi H., Ahmadi P.T., Yazdani N., Bayandori M., Rabiee N., Mobarakeh J.I. Smart drug delivery: capping strategies for mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2020;299 doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110115. - DOI
-
- Mladenović M., Morgan I., Ilić N., Saoud M., Pergal M.V., Kaluđerović G.N., Knežević N.Ž. pH-responsive release of ruthenium metallotherapeutics from mesoporous silica-based nanocarriers. Pharm. Times. 2021;13:460. https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/13/4/460 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Chen M., Kan Y., Dong Y., Zhang X., Wang X., Su H., Xu S., Yan X. Glutathione-responsive mesoporous silica nanocarriers for chemo–photothermal–photodynamic therapy of cancer. J. Mater. Sci. 2023;58:2764–2781. doi: 10.1007/s10853-023-08156-5. - DOI
-
- Knežević N.Ž. Visible light responsive anticancer treatment with an amsacrine-loaded mesoporous silica-based nanodevice. RSC Adv. 2013;3:19388–19392. doi: 10.1039/C3RA43492C. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

