Tracing knowledge diffusion trajectories in the research field of cyberbullying
- PMID: 39758416
- PMCID: PMC11699433
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41141
Tracing knowledge diffusion trajectories in the research field of cyberbullying
Abstract
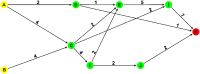
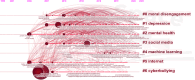
In today's digital age, cyberbullying has emerged as a pervasive issue that affects individuals across various social media platforms and digital communication channels. This review explores the developmental trajectory of cyberbullying as an interdisciplinary academic field, employing a unique combination of co-word analysis and main path analysis (MPA) across a substantial body of 5183 documents. This integrated methodological approach allows for a nuanced examination of the evolution of themes and influential works within the realm of cyberbullying research. The findings highlight a complex landscape where initial focus areas, such as the behavioral and psychological triggers of cyberbullying, progressively expand towards exploring effective preventive measures and intervention strategies. Key themes identified include the impact of digital literacy, the dual role of social media as both a vector and a tool against cyberbullying, and the potential of technological advancements in detecting and mitigating cyberbullying. This comprehensive mapping and analysis deepens our understanding of cyberbullying and highlights the dynamic nature of this field, suggesting new directions for future research and practical applications to effectively address cyberbullying across various social and technological contexts. This study represents a pioneering effort in synthesizing a broad spectrum of research to offer detailed insights into the changing dynamics of cyberbullying, marking a significant contribution to both academic knowledge and practical approaches to handling cyberbullying.
Keywords: Cyberbullying; Depression; Main path analysis; Psychology; Social media.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nursing in the digital age: The role of nursing in addressing cyberbullying and adolescents mental health.J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2025 Feb;32(1):57-70. doi: 10.1111/jpm.13085. Epub 2024 Jul 17. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39016201
-
Social media usage and cyberbullying: the moderating role of tie strength.Front Psychol. 2025 Feb 11;16:1490022. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1490022. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40008336 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the topical, conceptual, contextual, and methodological trends of cyberbullying research.J Commun Healthc. 2024 Dec;17(4):345-354. doi: 10.1080/17538068.2024.2393920. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Commun Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39166887
-
Implications and Preventions of Cyberbullying and Social Exclusion in Social Media: Systematic Review.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Jan 4;6(1):e30286. doi: 10.2196/30286. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 34982712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and Effect of Cyberbullying on Children and Young People: A Scoping Review of Social Media Studies.JAMA Pediatr. 2015 Aug;169(8):770-7. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.0944. JAMA Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 26098362
Cited by
-
Bullying and Cyberbullying Are Associated with Low Levels of Motivational Beliefs Toward Learning in Youth.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2025 May 23;15(6):93. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe15060093. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2025. PMID: 40558836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sabella R.A., Patchin J.W., Hinduja S. Cyberbullying myths and realities. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2013;29:2703–2711. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2013.06.040. - DOI
-
- Patchin J.W., Hinduja S. Bullies move beyond the schoolyard: a preliminary look at cyberbullying, youth violence juv. Justice. 2006;4:148–169. doi: 10.1177/1541204006286288. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources