The longitudinal relationship between executive dysfunction and reactive and proactive aggression in adolescents: impulsivity as a mediator and sex differences
- PMID: 39758445
- PMCID: PMC11695426
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1484340
The longitudinal relationship between executive dysfunction and reactive and proactive aggression in adolescents: impulsivity as a mediator and sex differences
Abstract
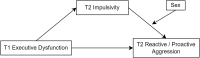
Background: Adolescent aggression poses a significant threat to mental health and social functioning. This study investigated the underlying mechanisms of reactive and proactive aggression in Chinese adolescents, focusing on the roles of executive dysfunction, impulsivity, and sex. We hypothesized that executive dysfunction would predict both reactive and proactive aggression, with impulsivity mediating these relationships. Furthermore, we explored the moderating role of sex in the association between impulsivity and both types of aggression.
Method: A longitudinal design with a 1-year follow-up was employed. The sample comprised 617 middle school students (mean age = 15.26 years at Time 2; 59% male). Participants completed self-report questionnaires at two time points (T1: April 2023; T2: April 2024): the Reactive-Proactive Aggression Questionnaire (RPQ), the Teenage Executive Functioning Inventory (TEXI), and the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale (BIS).
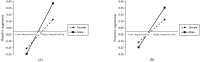
Results: Executive dysfunction at T1 significantly predicted both proactive and reactive aggression at T2. Impulsivity at T2 partially mediated the relationship between executive dysfunction at T1 and both proactive and reactive aggression at T2. Sex moderated the relationship between impulsivity and aggression. Specifically, impulsivity at T2 significantly predicted proactive aggression at T2 only in male adolescents. Impulsivity at T2 significantly predicted reactive aggression at T2 in both male and female adolescents, with a stronger effect observed in males.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that executive dysfunction contributes to adolescent aggression both directly and indirectly through increased impulsivity. Sex plays a moderating role, with male adolescents demonstrating greater vulnerability to the influence of impulsivity on aggression. These results underscore the importance of considering executive function, impulsivity, and sex in the development of interventions to prevent and reduce adolescent aggression.
Keywords: adolescents; executive dysfunction; impulsivity; proactive aggression; reactive aggression.
Copyright © 2024 Su, Li, Hu, Liu and Lian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Caregivers' Grit Moderates the Relationship Between Children's Executive Function and Aggression.Front Psychol. 2020 Apr 21;11:636. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00636. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32373017 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Media Violence, Narcissism and Sex on Reactive and Proactive Aggression in Adolescents: A One-Year Follow-Up Study.J Youth Adolesc. 2025 Apr;54(4):917-927. doi: 10.1007/s10964-024-02106-3. Epub 2024 Nov 2. J Youth Adolesc. 2025. PMID: 39487948
-
Factor Structure and Invariance of the Reactive and Proactive Aggression Questionnaire in a Large Sample of Young Adolescents in Singapore.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2016 Dec;47(6):883-889. doi: 10.1007/s10578-015-0619-y. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2016. PMID: 26702615
-
Perpetration of Adolescent Dating Violence: Child Abuse, Attitudes, Impulsivity, Reactive and Proactive Aggression; Automatic or Complex Processes?Aggress Behav. 2025 Jan;51(1):e70012. doi: 10.1002/ab.70012. Aggress Behav. 2025. PMID: 39660411
-
Associations among Parental Phubbing, Self-esteem, and Adolescents' Proactive and Reactive Aggression: A Three-Year Longitudinal Study in China.J Youth Adolesc. 2024 Feb;53(2):343-359. doi: 10.1007/s10964-023-01850-2. Epub 2023 Sep 11. J Youth Adolesc. 2024. PMID: 37697140
References
-
- Maji S, Bhattacharya S, Ghosh D. Cognitive coping and psychological problems among bullied and non-bullied adolescents. J Psychosocial Res. (2016) 11:387. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322603367.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

