Utilizing Medical Student Feedback to Improve Teaching Cases in Pre-clerkship Curricula
- PMID: 39758473
- PMCID: PMC11699177
- DOI: 10.1007/s40670-024-02128-3
Utilizing Medical Student Feedback to Improve Teaching Cases in Pre-clerkship Curricula
Abstract
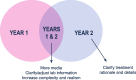
Feedback is an essential part of continuous quality improvement of cases used in medical curricula. This report describes results of qualitative analysis of feedback to elucidate what worked well and what needed improvement from the lens of our pre-clerkship medical students. Complexity, realism, and use of media were themes identified as strengths. Increasing the complexity, realism, and media as well as clarifying test results were themes for suggested improvements. While some feedback themes were similar across pre-clerkship years, others differed between first- and second-year students, likely representing the evolution of our learners.
Keywords: Active learning; Curriculum development; Educational scholarship; Pre-clinical medical education; Student-directed learning.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing InterestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources