Digital Ulcers and Microvascular Abnormalities Presenting As the Initial Manifestations of Pre-scleroderma
- PMID: 39759709
- PMCID: PMC11695195
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.75061
Digital Ulcers and Microvascular Abnormalities Presenting As the Initial Manifestations of Pre-scleroderma
Abstract
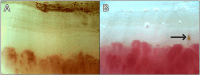
The term Raynaud's phenomenon (RP) is used to describe complex symptoms related to vascular compromise, which are typically exacerbated by cold-induced vasoconstriction, emotional stress, or other sympathomimetic factors. In almost all patients with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis (SSc), the first symptom is RP, often two to five years before any other symptom of scleroderma. The clinical course and severity of this disease are variable and highly fatal in some individuals, which has led to the development of strategies for timely diagnosis; hence, criteria for the very early diagnosis of systemic sclerosis have been established. Nevertheless, some individuals with this disease may lack classification findings (Raynaud's phenomenon, puffy fingers, and positive antinuclear antibodies), making their condition less apparent. This study reports a different clinical scenario involving a previously healthy 42-year-old woman with recent monophasic RP and digital ulcers in the absence of clinical or immunological manifestations of systemic autoimmune disease. The diagnosis of preclinical systemic sclerosis was made possible based on evidence of capillaroscopic abnormalities. The patient demonstrated favorable evolution following the initiation of treatment with hydroxychloroquine, a statin, and a calcium antagonist. Four years later, she had no recurrences of digital ulcers, a noticeable improvement in her RP, and no clinical features of systemic sclerosis, highlighting the paradigm of the natural history of scleroderma in its preclinical, clinical, advanced severe stages, and immunological abnormalities.
Keywords: immunosuppressive agents; nailfold videocapillaroscopy; raynaud's phenomenon; scleroderma; vasculopathy.
Copyright © 2024, Arango et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


References
-
- Raynaud's phenomenon - an update on diagnosis, classification and management. Pauling JD, Hughes M, Pope JE. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38:3317–3330. - PubMed
-
- Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Perelas A, Silver RM, Arrossi AV, Highland KB. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:304–320. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
