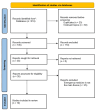
Precision Emergency Medicine: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39759728
- PMCID: PMC11698535
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.75068
Precision Emergency Medicine: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Precision medicine, which customizes healthcare based on individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, has significantly advanced various medical fields. However, its adoption in emergency medicine remains limited despite the potential to enhance patient outcomes through more accurate diagnostics and personalized treatments. This systematic review examined current evidence on the application of precision medicine in emergency care by analyzing studies published between 2010 and 2024. Out of 218 records, 10 studies met the inclusion criteria, highlighting areas such as genomic applications, machine learning, point-of-care diagnostics, and biomarkers. The findings indicate that precision medicine can improve diagnostic accuracy and personalize patient care in emergency settings, although challenges such as time constraints, technological limitations, and the need for enhanced clinician training remain. Overcoming these barriers through interdisciplinary collaboration, investment in rapid diagnostic technologies, and comprehensive education programs is essential for effectively integrating precision medicine into emergency care. Ultimately, advancing precision emergency medicine holds promise for transforming emergency care into a more personalized and effective practice, thereby improving patient outcomes in acute situations.
Keywords: emergency care; genomic medicine; personalized medicine; point-of-care diagnostics; precision emergency medicine; precision medicine; systematic review.
Copyright © 2024, Ahmed et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- National Research Council (US) Committee. National Academies Press. Washington (DC): National Academies Press; 2011. Toward Precision Medicine: Building a Knowledge Network for Biomedical Research and a New Taxonomy of Disease. - PubMed
-
- The growing role of emergency departments in hospital admissions. Schuur JD, Venkatesh AK. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:391–393. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous