Study of the Role of C-reactive Protein/Procalcitonin Ratio as a Prognostic Tool in ICU Patients with Sepsis: A Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 39759787
- PMCID: PMC11695878
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24855
Study of the Role of C-reactive Protein/Procalcitonin Ratio as a Prognostic Tool in ICU Patients with Sepsis: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Prediction of prognosis in sepsis is an essential research area aiming to improve disease outcomes. In this study, we investigated the role of the C-reactive protein (CRP)/procalcitonin (PCT) ratio as a prognostic tool in sepsis patients.
Materials and methods: This prospective observational study was conducted at the intensive care unit (ICU) of Alexandria Main University Hospital in the period from January to June 2024. One hundred and seventy patients with a diagnosis of sepsis were enrolled. Sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHEII) score and CRP/PCT ratio were calculated on admission (day 1), and as a follow-up on day 3. Patients were subsequently divided into survivor and non-survivor groups, and the data were compared.
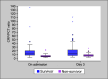
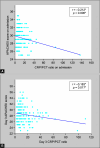
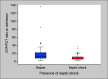
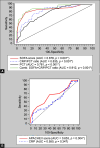
Results: The CRP/PCT ratio was significantly lower, on admission and on follow-up, in non-survivor patients than in survivor patients. The ratio median (minimum-maximum) in non-survivors was 4.82 (1.51-23.28) vs 11.23 (1.85-136.7) in survivors on admission, and it was 7.37 (2.27-26.36) in non-survivors vs 11.37 (2.78-110.9) in survivors on day 3. The ratio was significantly lower in patients with septic shock than in non-septic shock patients. The ratio had a significant negative correlation with both SOFA and APACHEII scores. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve showed high accuracy of the day 1 CRP/PCT ratio to predict mortality [area under curve (AUC = 0.835)], which is comparable to the day 1 SOFA score (AUC = 0.878) and higher than the day 1 PCT and day 1 APACHE scores.
Conclusion: Our results suggest a potential role for the CRP/PCT ratio, on admission and on follow-up, as a marker for predicting prognosis in sepsis patients, where low ratio values can predict poor disease outcome.
How to cite this article: Abdellatif EM, Hamouda EH. Study of the Role of C-reactive Protein/Procalcitonin Ratio as a Prognostic Tool in ICU Patients with Sepsis: A Prospective Observational Study. Indian J Crit Care Med 2024;28(12):1130-1138.
Keywords: C-reactive protein/PCT ratio; Intensive care unit; Procalcitonin; Prognosis; SOFA score; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2024; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: NoneConflict of interest: None
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Combined prognostic value of serum lactic acid, procalcitonin and severity score for short-term prognosis of septic shock patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Mar;33(3):281-285. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201113-00715. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 33834968 Chinese.
-
[The predictor value of peripheral blood procalcitonin levels in the evaluation of prognosis of patients with septic shock].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2012 Aug;24(8):470-3. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2012. PMID: 22871405 Chinese.
-
[Lactic acid, lactate clearance and procalcitonin in assessing the severity and predicting prognosis in sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Apr;32(4):449-453. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200129-00086. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32527351 Chinese.
-
[Prognostic value of Charlson weighted index of comorbidities combined with sequential organ failure assessment score and procalcitonin in patients with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Nov;31(11):1335-1339. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.11.005. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31898562 Chinese.
-
[The correlation between procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and severity scores in patients with sepsis and their value in assessment of prognosis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Feb;27(2):97-101. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.02.004. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 25665606 Chinese.
References
-
- Newman-Toker DE, Wang Z, Zhu Y, Nassery N, Saber Tehrani AS, Schaffer AC, et al. Rate of diagnostic errors and serious misdiagnosis-related harms for major vascular events, infections, and cancers: Toward a national incidence estimate using the “Big Three”. Diagnosis (Berl) 2021;8(1):67–84. doi: 10.1515/dx-2019-0104. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Souza DC, Jaramillo-Bustamante JC, Céspedes-Lesczinsky M, Quintero EMC, Jimenez HJ, Jabornisky R, et al. Challenges and health-care priorities for reducing the burden of paediatric sepsis in Latin America: A call to action. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2022;6(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/s2352-4642(21)00341-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
