Ossicular Chain Reconstruction With Glass Ionomer Cement Following Removal of Active Middle Ear Implant
- PMID: 39759944
- PMCID: PMC11696887
- DOI: 10.1002/oto2.70062
Ossicular Chain Reconstruction With Glass Ionomer Cement Following Removal of Active Middle Ear Implant
Abstract
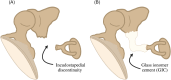
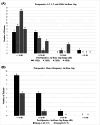
The use of bone cement in ossicular chain reconstruction (OCR) represents an area of recent interest. This multi-institutional retrospective study assesses the efficacy of glass ionomer cement (GIC) in OCR following the explantation of a fully implantable active middle ear implant. A postoperative 4-frequency mean air-bone gap (ABG) was obtained for 15 subjects by averaging 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 kHz frequencies. For Group A (short-term, N = 15), at a mean of 4.5 months postoperatively, 9 (60%) achieved an ABG between 0 and 10 dB, 5 (33%) were 11 to 20 dB, and 1 (7%) was 21 to 30 dB. For Group B (long-term, N = 5), at a mean of 50 months postoperatively, 4 (80%) were 0 to 10 dB and 1 (20%) was 11 to 20 dB. These results suggest that GIC represents an effective means of ABG closure after device explantation.
Keywords: Esteem®; active middle ear implant; audiometry; explant; glass ionomer cement; ossiculoplasty; rebridging; reconstruction.
© 2024 The Author(s). OTO Open published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
William J. McFeely Jr discloses that he is a consultant for Stryker Instruments, a division of Stryker Corporation. Jack A. Shohet discloses that he is a member of the Envoy Medical Advisory Board. Alexis E. McFeely declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

