Novel machine-learning model for predicting lymph node metastasis in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 39759999
- PMCID: PMC11693540
- DOI: 10.1002/ags3.12836
Novel machine-learning model for predicting lymph node metastasis in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Aim: Lymph node metastasis is an adverse prognostic factor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. However, it remains a challenge to predict lymph node metastasis using preoperative imaging alone. We used machine learning (combining preoperative imaging findings, tumor markers, and clinical information) to create a novel prediction model for lymph node metastasis in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Methods: The data of patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma who underwent surgery between September 1991 and October 2022 were retrospectively examined. Machine-learning software (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences Modeler) was used to create a prediction model, and parameter tuning was performed to improve the model's accuracy. We also analyzed the contribution of each feature to prediction using individual conditional expectation and partial dependence plots.
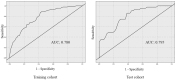
Results: Of the 331 cases included in the study, 241 comprised the training cohort and 90 comprised the test cohort. After parameter tuning, the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves for the training and test cohorts were 0.780 and 0.795, respectively. Individual conditional expectation and partial dependence plots showed that larger tumor size and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 and Duke pancreatic monoclonal antigen type 2 levels were associated with positive lymph node metastasis prediction in this model; neoadjuvant treatment was associated with negative lymph node metastasis prediction.
Conclusion: Machine learning may contribute to the creation of an effective predictive model of lymph node metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Prediction models using machine learning may contribute to the development of new treatment strategies in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: adenocarcinoma; early diagnosis; lymphatic metastasis; machine learning; pancreatic neoplasms.
© 2024 The Author(s). Annals of Gastroenterological Surgery published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Japanese Society of Gastroenterological Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this article. Itaru Endo is an editorial board member of the Annals of Gastroenterological Surgery.
Figures


References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Tempero MA, Malafa MP, al‐Hawary M, Behrman SW, Benson AB, Cardin DB, et al. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2021;19(4):439–457. - PubMed
-
- Yamada M, Sugiura T, Okamura Y, Ito T, Yamamoto Y, Ashida R, et al. Clinical implication of node‐negative Resectable pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021;28(4):2257–2264. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

