Longitudinal ozone exposure and SARS-CoV-2 infection in late pregnancy: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 39760090
- PMCID: PMC11695408
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1476603
Longitudinal ozone exposure and SARS-CoV-2 infection in late pregnancy: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Atmospheric ozone is a common air pollutant with known impacts on maternal and fetal health. However, the relationship between gestational ozone exposure and susceptibility to respirovirus infection remains unclear. This study aims to assess the association between longitudinal ozone exposure during pregnancy and COVID-19 risk in late gestation.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included 600 pregnant women (300 infected with SARS-CoV-2 and 300 uninfected) who delivered at one hospital in Jinan, China from November 2022 to January 2023. Individual ozone exposure levels throughout gestation were estimated based on local ambient monitoring data. Logistic regression models were constructed to examine the association between gestational ozone exposure and COVID-19 status in late pregnancy, adjusting for demographic and clinical variables.
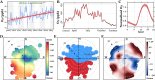
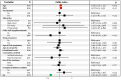
Results: In Jinan, ozone levels increased by 1.85 ppb annually and peaked between April and October, corresponding to winds from the south and southwest. Higher ozone exposure over pregnancy was associated with lower odds of SARS-CoV-2 infection in late gestation (OR per IQR increase = 0.60, 95% CI: 0.40-0.90). Compared to the lowest quartile (reference), the highest ozone quartile corresponded to a 99% decreased infection risk (OR = 0.01, 95% CI: 0.00-0.03). Increased maternal age and pre-pregnancy BMI were associated with higher COVID-19 risk.
Conclusions: Longitudinal ozone exposure during gestation may be protective against SARS-CoV-2 infection in late pregnancy. Further studies are needed to confirm this finding and elucidate underlying mechanisms. These results highlight the potential importance of environmental exposures in COVID-19 susceptibility.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 infection; environmental epidemiology; gestational ozone exposure; pregnancy outcomes; viral susceptibility.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Tian and Duan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen J., Guo L., Liu H., Jin L., Meng W., Fang J., et al. (2023). Modification effects of ambient temperature on associations of ambient ozone exposure before and during pregnancy with adverse birth outcomes: A multicity study in China. Environ. Int. 172, 107791. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2023.107791 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

