Betacoronavirus internal protein: role in immune evasion and viral pathogenesis
- PMID: 39760492
- PMCID: PMC11852921
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01353-24
Betacoronavirus internal protein: role in immune evasion and viral pathogenesis
Abstract
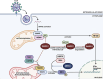
Betacoronaviruses express a small internal (I) protein that is encoded by the same subgenomic RNA (sgRNA) as the nucleocapsid (N) protein. Translation of the +1 reading frame of the N sgRNA through leaky ribosomal scanning leads to expression of the I protein. The I protein is an accessory protein reported to evade host innate immune responses during coronavirus infection. Previous studies have shown that the I proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), SARS-CoV-2, and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus suppress type I interferon production by distinct mechanisms. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on the I proteins of betacoronaviruses from different subgenera, with emphasis on its function and role in pathogenesis.
Keywords: coronavirus; immune evasion; internal protein; pathogenesis; virology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wong L-Y, Ye Z-W, Lui P-Y, Zheng X, Yuan S, Zhu L, Fung S-Y, Yuen K-S, Siu K-L, Yeung M-L, Cai Z, Woo P-Y, Yuen K-Y, Chan C-P, Jin D-Y. 2020. Middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus ORF8b accessory protein suppresses type I IFN expression by impeding HSP70-dependent activation of IRF3 kinase IKKε. J Immunol 205:1564–1579. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901489 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Shi Y, Pan X, Wu S, Hou R, Zhang Y, Zhong T, Tang H, Du W, Wang L, Wo J, Mu J, Qiu Y, Yang K, Zhang L-K, Ye B-C, Qi N. 2021. SARS-CoV-2 ORF9b inhibits RIG-I-MAVS antiviral signaling by interrupting K63-linked ubiquitination of NEMO. Cell Rep 34:108761. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108761 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

