Pediatric Myeloid Neoplasms With UBTF Tandem Duplications : Morphologic, Immunophenotypic, and Clinical Characterization
- PMID: 39760616
- PMCID: PMC11893000
- DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000002350
Pediatric Myeloid Neoplasms With UBTF Tandem Duplications : Morphologic, Immunophenotypic, and Clinical Characterization
Abstract
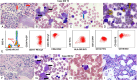
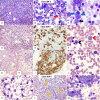
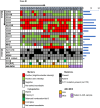
Tandem duplications (TDs) in exons of upstream binding transcription factor ( UBTF -TD) are a rare recurrent alteration in pediatric and adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)/neoplasm. Although recently identified, AML with UBTF -TD is now considered a distinct subtype of AML. To further our understanding of myeloid neoplasms with UBTF -TD, we analyzed clinical, morphologic, and immunophenotypic characteristics of 27 pediatric patients with UBTF- TD-positive myeloid neoplasm, including 21 diagnosed as AML and 6 as MDS. Our data demonstrated that UBTF -TD is frequently associated with cytopenia, hypercellular marrow with erythroid hyperplasia, and trilineage dysplasia. Blasts and maturing myeloid cells show a characteristic dysplastic feature with condensed eosinophilic cytoplasm. Blasts have a myeloid or myelomonocytic immunophenotype with a variably dim expression of CD34 and/or CD117, and except for CD7 expression lack a consistent pattern of aberrant lineage-specific antigen expression. Patients with MDS had a lower blast count in the peripheral blood ( P = 0.03) and bone marrow ( P <0.001) but otherwise had no significant differences in other hematological parameters. Three patients with MDS rapidly progressed to AML in 33, 39, and 210 days from the initial diagnosis and there was no difference in overall survival between patients with MDS and AML ( P = 0.18). Our data suggest that MDS with UBTF-TD is prognostically equivalent to AML with UBTF -TD and thus should be considered as a continuum of the same molecularly defined myeloid neoplasm. These collective data also provide morphologic and immunophenotypic clues that can prompt screening for UBTF -TD in patients with MDS or AML.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest and Source of Funding: J.M.K. and M.U.: Honorarium, AstraZeneca Japan. J.M.K. holds a Career Award for Medical Scientists from the Burroughs Wellcome Fund. For the remaining authors, none were declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thrombopoietin mimetics for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 30;9(9):CD009883. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009883.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28962071 Free PMC article.
-
Acute myeloid leukemias with UBTF tandem duplications are sensitive to menin inhibitors.Blood. 2024 Feb 15;143(7):619-630. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023021359. Blood. 2024. PMID: 37890156 Free PMC article.
-
The Significance of Detecting an Unusual Myeloblast Immunophenotype in a Presumptive Clinical Diagnosis of Myelodysplastic Syndromes.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2025 Aug 1;149(8):717-726. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2024-0228-OA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2025. PMID: 39711284
-
UBTF tandem duplications in pediatric myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia: implications for clinical screening and diagnosis.Haematologica. 2024 Aug 1;109(8):2459-2468. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2023.284683. Haematologica. 2024. PMID: 38426285 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-2 as maintenance therapy for children and adults with acute myeloid leukaemia in first complete remission.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 6;2015(11):CD010248. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010248.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26544114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanij E, Hannan RD. The role of UBF in regulating the structure and dynamics of transcriptionally active rDNA chromatin. Epigenetics. 2009;4:374–382. - PubMed
-
- Kaburagi T, Shiba N, Yamato G, et al. . UBTF-internal tandem duplication as a novel poor prognostic factor in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2023;62:202–209. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

