Luteimonas salinilitoris sp. nov., isolated from the shore soil of saline lake in Tibet of China
- PMID: 39760639
- PMCID: PMC12281983
- DOI: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006630
Luteimonas salinilitoris sp. nov., isolated from the shore soil of saline lake in Tibet of China
Abstract
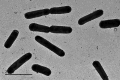
Five aerobic, Gram-stain-negative bacterial strains, designated as C3-2-a3T, B3-2-R+30, C3-2-a4, C3-2-M3 and C3-2-M8, were isolated from the coastal soil of LungmuCo Lake in the Tibet Autonomous Region, PR China. Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA genes and genomes indicated that these isolates belonged to the genus Luteimonas and showed a high similarity to Luteimonas suaedae LNNU 24178T (99.01%), Luteimonas endophytica RD2P54T (98.80%) and Luteimonas salinisoli SJ-92T (97.67%). The average nucleotide identity (ANI) and digital DNA-DNA hybridization (dDDH) values between strain C3-2-a3T and related reference strains Luteimonas suaedae LNNU 24178T, Luteimonas endophytica RD2P54T and Luteimonas salinisoli SJ-92T were 91.89, 83.11 and 83.86% and 46.90, 26.90 and 28.20%, respectively. All values were below the thresholds for delineating species, supporting their classification as novel species of the genus Luteimonas. The genomic DNA G+C content of strains C3-2-a3T was 68.39%. The major polar lipids were diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine and two unidentified phospholipids. The predominant respiratory quinone was ubiquinone-8 (Q-8), aligning with the characteristics of members of the genus Luteimonas. The major fatty acids (>10.0%) of strain C3-2-a3T were identified as iso-C11 : 0, iso-C15 : 0, iso-C16 : 0 and iso-C17 : 1 ω9c. Based on the results of phenotypic, physiological, chemotaxonomic and genotypic characterizations, we propose that the isolates represent a novel species of genus Luteimonas, for which the name Luteimonas salinilitoris sp. nov is proposed. The type strain is C3-2-a3T (=CGMCC 1.14507T=KCTC 8642T).
Keywords: Luteimonas salinilitorissp. nov.; Tibet; saline lake; soil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Algoriphagus aurantiacus sp. nov. and Algoriphagus persicinus sp. nov., two novel species isolated from the shore soil of salt lake.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025 Jun;75(6):006826. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006826. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40577042 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudidiomarina salilacus sp. nov., a novel bacterium of the genus Pseudidiomarina isolated from sediment in Yuncheng Salt Lake.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025 Jul;75(7). doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006846. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40673902
-
Luteimonas suaedae sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from rhizosphere of Suaeda aralocaspica (Bunge) Freitag & Schütze.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2023 Oct;73(10). doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006088. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37831063
-
Variovorax atrisoli sp. nov., a novel species isolated from black soil applied with herbicide atrazine in Northeast China.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025 Aug;75(8). doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006886. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40787852
-
Phylotaxonomic analysis uncovers underestimated species diversity within the genus Rossellomorea with description of selenium-resistant Rossellomorea yichunensis sp. nov.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):408. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04138-6. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40610858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Finkmann W, Altendorf K, Stackebrandt E, Lipski A. Characterization of N2O-producing Xanthomonas-like isolates from biofilters as Stenotrophomonas nitritireducens sp. nov., Luteimonas mephitis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Pseudoxanthomonas broegbernensis gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000;50:273–282. doi: 10.1099/00207713-50-1-273. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

