Study of Different Cultivated Plants Rhizosphere Soil Fungi-Mediated Pectinase: Insights into Production, Optimization, Purification, Biocompatibility, and Application
- PMID: 39760871
- PMCID: PMC11703994
- DOI: 10.1007/s00248-024-02474-0
Study of Different Cultivated Plants Rhizosphere Soil Fungi-Mediated Pectinase: Insights into Production, Optimization, Purification, Biocompatibility, and Application
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Study of Different Cultivated Plants Rhizosphere Soil Fungi-Mediated Pectinase: Insights into Production, Optimization, Purification, Biocompatibility, and Application.Microb Ecol. 2025 Jan 28;87(1):180. doi: 10.1007/s00248-025-02498-0. Microb Ecol. 2025. PMID: 39873755 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
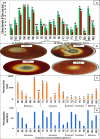
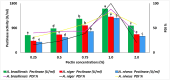
Microorganisms are preferred as an enzyme source due to their short lifespan, high production rate, affordability, and absence of harmful chemicals in enzymes generated from plant and animal sources. Fungi communities are biological factories for many bioactive compounds such as the important industrial enzyme pectinase. The current study dealt with production, optimization, purification, biocompatibility, and application of fungal pectinase obtained from five plant rhizospheres (banana, jarawa, lemon, tomato, and wheat) at Fayoum Governorate, Egypt. The highest pectinase degrading index (PDI) was scored for FB5, FJ2, and FW1 isolates. Pectinase production was also examined quantitively and the highest output of 1603.67, 1311.22, and 1264.83 U/ml was gained by FB5, FJ1, and FW1 fungal isolates, respectively. The most active pectinase-producing fungi were identified as Aspergillus niveus strain AUMC1624, A. niger strain AUMC16245, and A. brasiliensis strain AUMC16244, respectively. For pectinase production optimization, one factor at a time (OFAT) protocol was applied and revealed that A. niger, A. niveus, and A. brasiliensis reached maximum pectinase levels at 1% pectin after 5, 7, and 7 days, at 40, 45, and 45 °C, respectively. Obtained pectinases were partially purified using ammonium sulfate precipitation (ASP) and organic solvent precipitation (OSP) methods. The highest activity using the ASP method scored at 40-60% saturation with A. niger. The thermostability characterization of A. niger pectinase was reached with relative activities of 61.7, 69.0, 99.9, 91.3, and 90.6% at temperatures ranging between 30 and 70 °C. pH optimized at pH 5-7. The enzyme's molecular weight was approximately 30 kDa. The GC-mass analysis of pectinase end products included acetic acid ethyl ester, hexadecane carbonsaure methylase, and hexadecenoic acid. The biocompatibility was examined using a human skin cell line (HFb-4) for the first time, with a minimal half concentration (IC50) of 151.86 ± 0.76 U/ml. The biocompatible pectinase was applied as a clothes bioscouring agent with different concentrations of 1893.52 U/ml achieving the highest bioscouring with 20.0%.
Keywords: Bioscouring; Human skin cell line (HFb-4); Microorganisms; Pectinase; Rhizosphere.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical Approval: There are no studies of this article that include human subjects or animals. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- AbdRahman NH, Rahman RA, Rahmat Z et al (2024) Innovative biocatalyst synthesis of pectinolytic enzymes by cross-linking strategy: potentially immobilised pectinases for the production of pectic-oligosaccharides from pectin. Inter J Biolog Macromol 256:128260. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128260 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kavuthodi B, Sebastian D (2018) Review on bacterial production of alkaline pectinase with special emphasis on Bacillus species. Biosci Biotech Res Commun 11:18–30. 10.21786/bbrc/11.1/4 - DOI
-
- Mondal S, Halder SK, Mondal KC (2024) Recombinant fungal pectinase and their role towards fostering modern agriculture. In Entrepreneurship with Microorganisms (pp 405–418). 10.1016/b978-0-443-19049-0.00003-7
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

