Metabolomics analyses and comparative insight to neuroprotective potential of unripe fruits and leaves of Citrus aurantium ethanolic extracts against cadmium-induced rat brain dysfunction: involvement of oxidative stress and akt-mediated CREB/BDNF and GSK3β/NF-κB signaling pathways
- PMID: 39760898
- PMCID: PMC11703990
- DOI: 10.1007/s11011-024-01513-6
Metabolomics analyses and comparative insight to neuroprotective potential of unripe fruits and leaves of Citrus aurantium ethanolic extracts against cadmium-induced rat brain dysfunction: involvement of oxidative stress and akt-mediated CREB/BDNF and GSK3β/NF-κB signaling pathways
Abstract
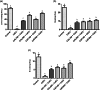
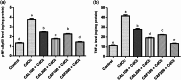
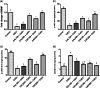
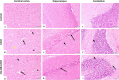
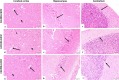
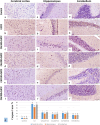
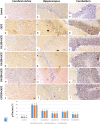
Serious neurological disorders were associated with cadmium toxicity. Hence, this research aimed to investigate the potential neuroprotective impacts of the ethanolic extracts of Citrus aurantium unripe fruits and leaves (CAF and CAL, respectively) at doses 100 and 200 mg/kg against cadmium chloride-provoked brain dysfunction in rats for 30 consecutive days. HPLC for natural pigment content revealed that CAF implied higher contents of Chlorophyll B, while the CAL has a high yield of chlorophyll A and total carotenoid. Fifty-seven chromatographic peaks were identified by UPLC/MS/MS; 49 and 29 were recognized from CAF or CAL, respectively. Four compounds were isolated from CAF: 3',4',7 -trihydroxyflavone, isorhainetin, vitexin, and apigenin. In vitro studies outlined the antioxidant capacity of studied extracts where CAF showed better scavenging radical DPPH activity. Results clarified that both extracts with a superior function of CAF at the high adopted dose significantly ameliorated CdCl2-induced neuro-oxidative stress and neuro-inflammatory response via restoring antioxidant status and hindering nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) stimulation. Moreover, it up-regulated the levels of phospho-protein kinase B (p-Akt), phospho- cAMP-response element binding protein (p-CREB), and brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) levels, and elicited a marked decrease in the content of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β), besides amending Caspase-3 and hyperphosphorylation of tau protein in brain tissues. Moreover, a significant improvement in the rats' behavioral tasks of the CAL and CAF-treated groups has been recorded, as indicated by marked preservation in locomotion, exploratory, and memory functions of the experimental rats. In conclusion, the reported neuroprotective impacts of C. aurantium extracts may be through modulating p-AKT/p-CREB/BDNF and / or p-Akt/ GSK3β/NF-κB signaling pathways.
Keywords: Citrus aurantium; Cadmium; Cognitive function; Flavonoids; Neurotoxicity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: This work was carried out in compliance with the ethical procedures and policies delineated in the National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of Laboratory animals (NIH Publications No. 8023, revised 1978)., the ARRIVE guidelines and international legislation, which approved by the Medical Research Ethics (MREC) Committee of the National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, Egypt (Approval no. 7441201-2023). Consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent to Publish: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
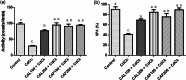
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

