Development of nucleus-targeted histone-tail-based photoaffinity probes to profile the epigenetic interactome in native cells
- PMID: 39762271
- PMCID: PMC11704063
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55046-8
Development of nucleus-targeted histone-tail-based photoaffinity probes to profile the epigenetic interactome in native cells
Abstract
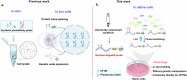
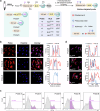
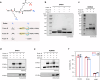
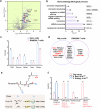
Dissection of the physiological interactomes of histone post-translational modifications (hPTMs) is crucial for understanding epigenetic regulatory pathways. Peptide- or protein-based histone photoaffinity tools expanded the ability to probe the epigenetic interactome, but in situ profiling in native cells remains challenging. Here, we develop a nucleus-targeting histone-tail-based photoaffinity probe capable of profiling the hPTM-mediated interactomes in native cells, by integrating cell-permeable and nuclear localization peptide modules into an hPTM peptide equipped with a photoreactive moiety. These types of probes, such as histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation and histone H3 Lysine 9 crotonylation probes, enable the probing of epigenetic interactomes both in HeLa cell and hard-to-transfect RAW264.7 cells, resulting in the discovery of distinct interactors in different cell lines. The utility of this probe is further exemplified by characterizing interactome of emerging hPTM, such as AF9 was detected as a binder of histone H3 Lysine 9 lactylation, thus expanding the toolbox for profiling of hPTM-mediated PPIs in live cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell128, 693–705 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Lin, J. et al. Menin “reads” H3K79me2 mark in a nucleosomal context. Science379, 717–723 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Boichenko, I. & Fierz, B. Chemical and biophysical methods to explore dynamic mechanisms of chromatin silencing. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol.51, 1–10 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

