Development and validation of a nomogram to predict survival in septic patients with heart failure in the intensive care unit
- PMID: 39762511
- PMCID: PMC11704260
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-85596-w
Development and validation of a nomogram to predict survival in septic patients with heart failure in the intensive care unit
Abstract
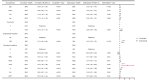
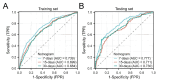
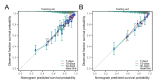
Heart failure is a common complication in patients with sepsis, and individuals who experience both sepsis and heart failure are at a heightened risk for adverse outcomes. This study aims to develop an effective nomogram model to predict the 7-day, 15-day, and 30-day survival probabilities of septic patients with heart failure in the intensive care unit (ICU). This study extracted the pertinent clinical data of septic patients with heart failure from the Critical Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC-IV) database. Patients were then randomly allocated into a training set and a test set at a ratio of 7:3. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was used to determine independent risk factors influencing patient prognosis and to develop a nomogram model. The model's efficacy and clinical significance were assessed through metrics such as the concordance index (C-index), time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC), calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA). A total of 5,490 septic patients with heart failure were included in the study. A nomogram model was developed to predict short-term survival probabilities, using 13 variables: age, pneumonia, endotracheal intubation, mechanical ventilation, potassium (K), anion gap (AG), lactate (Lac), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), white blood cell count (WBC), red cell distribution width (RDW), hemoglobin-to-red cell distribution width ratio (HRR), Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score, and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI). The C-index was 0.730 (95% CI 0.719-0.742) for the training set and 0.761 (95% CI 0.745-0.776) for the test set, indicating strong model accuracy, indicating good model accuracy. Evaluations via the ROC curve, calibration curve, and decision curve analyses further confirmed the model's reliability and utility. This study effectively developed a straightforward and efficient nomogram model to predict the 7-day, 15-day, and 30-day survival probabilities of septic patients with heart failure in the ICU. The implementation of treatment strategies that address the risk factors identified in the model can enhance patient outcomes and increase survival rates.
Keywords: Heart failure; MIMIC-IV database; Nomogram model; Retrospective analysis; Sepsis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Development and validation of a prognostic model for patients with sepsis in intensive care unit].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Aug;35(8):800-806. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20230103-00003. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37593856 Chinese.
-
A nomogram for predicting short-term mortality in ICU patients with coexisting chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and congestive heart failure.Respir Med. 2024 Nov-Dec;234:107803. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2024.107803. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Respir Med. 2024. PMID: 39251097
-
[Establishment of a nomogram prediction model for 28-day mortality of septic shock patients based on routine laboratory data mining].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Nov;36(11):1127-1132. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240202-00108. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39697015 Chinese.
-
[Development and validation of a nomogram prediction model for in-hospital mortality risk in patients with sepsis complicated with acute pulmonary embolism].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025 Feb;37(2):123-127. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240918-00778. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025. PMID: 40017358 Chinese.
-
[Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting 3-month mortality risk in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 May;36(5):465-470. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20231218-01091. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 38845491 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Enhancing prognostic accuracy in sepsis: a modified SOFA score incorporating lymphocyte count as an immune function marker.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jul 31;15:1593589. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1593589. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40822591 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

