Effectiveness and tolerability of rimegepant in the acute treatment of migraine: a real-world, prospective, multicentric study (GAINER study)
- PMID: 39762740
- PMCID: PMC11702052
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-024-01935-8
Effectiveness and tolerability of rimegepant in the acute treatment of migraine: a real-world, prospective, multicentric study (GAINER study)
Abstract
Background: Rimegepant, a novel oral calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist, has been recently approved for the acute migraine treatment. While its efficacy was confirmed in randomized clinical trials, no data is available regarding real-life effectiveness and tolerability. GAINER, a prospective, multicentric study, aimed to evaluate rimegepant effectiveness and tolerability in the real-world setting.
Methods: Our study involved 16 headache centers across Italy. The main outcomes were: i) 2 h pain freedom, and ii) occurrence of treatment-emergent adverse events after administration. Participants were instructed to treat one migraine attack with rimegepant 75 mg orally disintegrating tablet. Using an ad hoc diary, participants prospectively collected migraine attack features at baseline and every 30 min after rimegepant administration, up to 2 h post dose. A 24 h follow up was also collected.
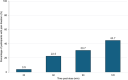
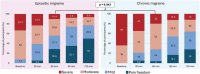
Results: We enrolled 103 participants with migraine (74.8% female, mean age 44.4 [42.0 - 46.7] years, 24.3% with chronic migraine of whom 44.0% presented a concomitant diagnosis of medication overuse headache). The number of previously failed preventive classes was 2.7 [2.3 - 3.2]. Participants presented a mean of 9.6 [8.2 - 10.9] monthly migraine days at baseline. At rimegepant intake, 40.8% of patients rated migraine intensity as severe. Pain freedom 2 h post dose was reported in 44.7% (46/103) of individuals. Pain freedom 2 h post dose was not influenced by baseline pain severity (p = 0.316), but it was associated with timing of intake (p = 0.032) with a higher rate of 2 h pain freedom when rimegepant was taken within 1 h from pain onset. Mild adverse events were reported in 15.5% total attacks (16/103), predominantly fatigue (n = 6), gastrointestinal symptoms (n = 6), somnolence (n = 4), and transient cognitive difficulties (n = 3). Tolerability was rated as good-to-excellent in 85.4% cases (88/103).
Conclusions: Our data confirms rimegepant effectiveness and safety in the acute migraine treatment in a real-world setting in a cohort of participants that includes subjects with episodic or chronic migraine, medication overuse and a high number of prior preventive treatment failures.
Trial registration: The study was preregistered on clinicaltrial.gov, NCT05903027.
Keywords: Acute treatments; CGRP; Gepants; Triptans.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved as a part of the Registro Italiano Cefalee (RICe) study by the local Ethics Committee (CEAVC Studio RICe, 14591_oss and subsequent amendments 2022–609; 2023). Competing interests: LFI received fees and Honoraria for advisory boards, speaker panels from Teva, Eli Lilly, Lundbeck, Pfizer and AbbVie. GV received personal fees from Lundbeck; M.S has received speaker honoraria from Novartis, Teva, and Lilly; AR has received speaker honoraria from Allergan, Lilly, Novartis, Biogen, and Teva and serves as an associate editor of Frontiers in Neurology (Headache Medicine and Facial Pain session); SC received honoraria for speaker panels from Teva and Novartis; MPP received speaker honoraria and advisory board participation from Abbvie, Idorsia, Eli-Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, TEVA; RO reports personal fees and non-financial support from Allergan-AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Teva; RDI reports personal fees and non-financial support from Eli-Lilly, AbbVie, Pfizer, Lundbeck, and TEVA. Other authors have no conflicting interests on this specific study.
Figures


References
-
- Ashina AM (2020) Migraine. N Engl J Med 383(19):1866–1876 - PubMed
-
- Ailani J (2021) Acute migraine treatment. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 27(3):597–612 - PubMed
-
- Affaitati G, Martelletti P, Lopopolo M, Tana C, Massimini F, Cipollone F et al (2017) Use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for symptomatic treatment of episodic headache. Pain Pract 17(3):392–401 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

