Biglycan-driven risk stratification in ZFTA-RELA fusion supratentorial ependymomas through transcriptome profiling
- PMID: 39762990
- PMCID: PMC11706152
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-024-01921-w
Biglycan-driven risk stratification in ZFTA-RELA fusion supratentorial ependymomas through transcriptome profiling
Erratum in
-
Correction: Biglycan-driven risk stratification in ZFTA-RELA fusion supratentorial ependymomas through transcriptome profiling.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025 Aug 21;13(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-02094-w. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40841695 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
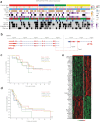
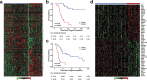
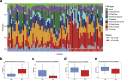
Recent genomic studies have allowed the subdivision of intracranial ependymomas into molecularly distinct groups with highly specific clinical features and outcomes. The majority of supratentorial ependymomas (ST-EPN) harbor ZFTA-RELA fusions which were designated, in general, as an intermediate risk tumor variant. However, molecular prognosticators within ST-EPN ZFTA-RELA have not been determined yet. Here, we performed methylation-based DNA profiling and transcriptome RNA sequencing analysis of 80 ST-EPN ZFTA-RELA investigating the clinical significance of various molecular patterns. The principal types of ZFTA-RELA fusions, based on breakpoint location, demonstrated no significant correlations with clinical outcomes. Multigene analysis disclosed 1892 survival-associated genes, and a metagene set of 100 genes subdivided ST-EPN ZFTA-RELA into favorable and unfavorable transcriptome subtypes composed of different cell subpopulations as detected by deconvolution analysis. BGN (biglycan) was identified as the top-ranked survival-associated gene and high BGN expression levels were associated with poor survival (Hazard Ratio 17.85 for PFS and 45.48 for OS; log-rank; p-value < 0.01). Furthermore, BGN immunopositivity was identified as a strong prognostic indicator of poor survival in ST-EPN, and this finding was confirmed in an independent validation set of 56 samples. Our results indicate that integrating BGN expression (at mRNA and/or protein level) into risk stratification models may improve ST-EPN ZFTA-RELA outcome prediction. Therefore, gene and/or protein expression analyses for this molecular marker could be adopted for ST-EPN ZFTA-RELA prognostication and may help assign patients to optimal therapies in prospective clinical trials.
Keywords: BGN; ZFTA-RELA fusion; Ependymoma; Expression; Prognosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted under the auspices of the local Ethics Committees, in compliance with German rules of the Health Insurance Portability. Consent for publication: All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with its submission. Competing interests: Felix Sahm is co-founder and shareholder of Heidelberg Epignostix GmbH.
Figures

References
-
- Andreiuolo F, Varlet P, Tauziède-Espariat A, Jünger ST, Dörner E, Dreschmann V, Kuchelmeister K, Waha A, Haberler C, Slavc I (2019) Childhood supratentorial ependymomas with YAP1‐MAMLD1 fusion: an entity with characteristic clinical, radiological, cytogenetic and histopathological features. Brain Pathol 29:205–216 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batchu S, Patel K, Yu S, Mohamed AT, Karsy M (2022) Single cell transcriptomics reveals unique metabolic profiles of ependymoma subgroups. Gene 820:146278 - PubMed
-
- Chapman RJ, Ghasemi DR, Andreiuolo F, Zschernack V, Espariat AT, Buttarelli FR, Giangaspero F, Grill J, Haberler C, Paine SM (2023) Optimizing biomarkers for accurate ependymoma diagnosis, prognostication, and stratification within international clinical trials: a BIOMECA study. Neurooncology 25:1871–1882 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

