G9a an Epigenetic Therapeutic Strategy for Neurodegenerative Conditions: From Target Discovery to Clinical Trials
- PMID: 39763018
- PMCID: PMC11976383
- DOI: 10.1002/med.22096
G9a an Epigenetic Therapeutic Strategy for Neurodegenerative Conditions: From Target Discovery to Clinical Trials
Abstract
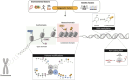
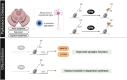
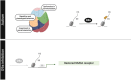
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the role of G9a/EHMT2, focusing on its structure and exploring the impact of its pharmacological and/or gene inhibition in various neurological diseases. In addition, we delve into the advancements in the design and synthesis of G9a/EHMT2 inhibitors, which hold promise not only as a treatment for neurodegeneration diseases but also for other conditions, such as cancer and malaria. Besides, we presented the discovery of dual therapeutic approaches based on G9a inhibition and different epigenetic enzymes like histone deacetylases, DNA methyltransferases, and other lysine methyltransferases. Hence, findings offer valuable insights into developing novel and promising therapeutic strategies targeting G9a/EHMT2 for managing these neurological conditions.
Keywords: EHMT2; G9a; aging; clinical trials; epigenetics; neurodegenerative conditions; small‐molecules.
© 2025 The Author(s). Medicinal Research Reviews published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures







References
-
- Deuschl G., Beghi E., Fazekas F., et al., “The Burden of Neurological Diseases in Europe: An Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017,” Lancet Public Health 5, no. 10 (2020): e551–e567. - PubMed
-
- Shademan B., Biray Avci C., Nikanfar M., and Nourazarian A., “Application of Next‐Generation Sequencing in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Opportunities and Challenges,” NeuroMolecular Medicine 23, no. 2 (2021): 23225–23235. - PubMed
-
- Hou Y., Dan X., Babbar M., et al., “Ageing as a Risk Factor for Neurodegenerative Disease,” Nature Reviews Neurology 15, no. 10 (2019): 565–581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

